Amlodipine benazepril is widely recognized for its dual action in managing hypertension and heart failure. Expect effective blood pressure control as it combines the benefits of a calcium channel blocker, amlodipine, with the ACE inhibitor, benazepril. This combination works by relaxing blood vessels and reducing the workload on the heart. Regular monitoring of blood pressure is recommended to evaluate the medication’s effectiveness and adjust dosages as needed.
Patients should take this medication consistently to maintain stable blood pressure levels. It is advisable to start with the lowest dose, then gradually increase under medical supervision. Drinking alcohol may enhance side effects such as dizziness or lightheadedness, so moderation is key. Furthermore, staying hydrated while on this medication can help mitigate potential side effects associated with dehydration.
Be aware of potential interactions with other medications. Inform your healthcare provider about all medications and supplements you’re taking. Engaging in healthy lifestyle choices, such as a balanced diet and regular exercise, can significantly enhance the benefits of amlodipine benazepril. Always consult with a healthcare professional before making any changes to your treatment plan.
- Amlodipine Benazepril: A Comprehensive Overview
- Understanding Amlodipine and Benazepril Components
- Mechanism of Action for Amlodipine Benazepril Combination
- Indications for Using Amlodipine Benazepril in Hypertension
- Dosage Guidelines and Administration Tips
- Potential Side Effects and Interactions to Monitor
- Common Side Effects
- Drug Interactions
- Patient Compliance and Lifestyle Considerations
Amlodipine Benazepril: A Comprehensive Overview
Amlodipine benazepril combines two medications to treat high blood pressure and certain heart conditions. This combination works by relaxing blood vessels and reducing strain on the heart. Amlodipine, a calcium channel blocker, prevents calcium from entering heart and blood vessel cells, leading to smoother blood flow. Benazepril, an ACE inhibitor, inhibits the production of angiotensin II, a substance that narrows blood vessels. This dual action effectively lowers blood pressure and improves oxygen delivery to the heart.
Patients typically start with a low dose to minimize side effects. Common side effects include dizziness, fatigue, and swelling in the legs. If side effects persist or worsen, consult a healthcare provider for adjustments. Regular monitoring of blood pressure is essential to evaluate the medication’s effectiveness and to ensure dosages remain appropriate.
For those with specific conditions like heart failure or kidney problems, this combination might provide better management. Always inform your doctor of any other medications you are taking, including over-the-counter drugs and supplements, to avoid harmful interactions.
Hydration plays a key role while using amlodipine benazepril. Staying well-hydrated can help minimize some side effects and enhance the medication’s overall effectiveness. Patients should prioritize a balanced diet rich in fruits, vegetables, and low-sodium options to complement treatment and promote heart health.
If pregnancy is a possibility, discuss alternatives with your healthcare provider, as this medication may pose risks. Stopping the medication suddenly can cause blood pressure to spike; any changes should be managed under professional supervision.
Incorporating lifestyle changes, such as regular exercise and smoking cessation, significantly boosts the benefits of amlodipine benazepril. Adopting healthy habits not only improves blood pressure control but also supports overall cardiovascular health. Regular check-ups remain essential in monitoring heart health and medication efficacy.
Understanding Amlodipine and Benazepril Components
Amlodipine acts as a calcium channel blocker, widening blood vessels and improving blood flow. This mechanism helps to lower blood pressure efficiently. Patients often experience a reduction in symptoms related to hypertension, such as headaches and dizziness.
Benazepril belongs to the class of medications known as ACE inhibitors. It prevents the conversion of angiotensin I to angiotensin II, a substance that narrows blood vessels. By inhibiting this process, benazepril relaxes blood vessels, which aids in lowering blood pressure and protecting kidney function.
Combining amlodipine and benazepril enhances their individual effects. This combination can lead to superior management of high blood pressure compared to either drug alone. Doctors frequently prescribe this combination for patients whose hypertension may not respond to monotherapy.
Side effects may include dizziness, fatigue, or swelling in the extremities. Patients should monitor their response to the medication and communicate any unusual symptoms to their healthcare provider promptly.
Regular follow-ups with blood pressure checks are essential after starting this combination therapy. Adjusting doses based on individual response ensures optimal blood pressure control and minimizes risks associated with elevated levels.
Incorporating lifestyle changes, such as a balanced diet and regular exercise, enhances the effectiveness of amlodipine and benazepril. Patients should also remain vigilant about weight management and sodium intake.
Mechanism of Action for Amlodipine Benazepril Combination
Amlodipine benazepril combines the properties of two distinct medications: amlodipine, a calcium channel blocker, and benazepril, an ACE inhibitor. This combination effectively manages hypertension and heart failure by targeting different pathways in the cardiovascular system.
Amlodipine works by inhibiting calcium ions from entering vascular smooth muscle and cardiac muscle. This leads to vasodilation, effectively reducing peripheral resistance and decreasing blood pressure. It also enhances blood flow to the heart by dilating coronary arteries.
Benazepril, on the other hand, inhibits the angiotensin-converting enzyme (ACE), which plays a role in converting angiotensin I to angiotensin II. Angiotensin II constricts blood vessels and stimulates aldosterone secretion, promoting sodium retention and increasing blood volume. By blocking this conversion, benazepril lowers blood pressure and reduces the workload on the heart.
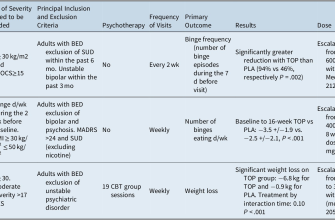
| Drug | Class | Mechanism of Action | Effects |
|---|---|---|---|
| Amlodipine | Calcium Channel Blocker | Blocks calcium entry into cells | Vasodilation, reduced peripheral resistance |
| Benazepril | ACE Inhibitor | Inhibits the conversion of angiotensin I to II | Lower blood pressure, reduced blood volume |
The synergy of these two medications enhances overall antihypertensive effects. Patients experience improved outcomes with lower dosages of each drug, resulting in reduced side effects while maintaining optimal blood pressure control.
This combination therapy not only addresses hypertension but also provides protective effects on the heart, making it a practical choice for managing conditions like heart failure and diabetic kidney disease.
Indications for Using Amlodipine Benazepril in Hypertension
Amlodipine benazepril is indicated for the management of hypertension, especially in patients who may benefit from dual therapy targeting distinct mechanisms. The combination acts as a calcium channel blocker and an ACE inhibitor, providing complementary effects. This synergy can enhance blood pressure control while minimizing adverse effects.
Patients with essential hypertension often experience better outcomes with this combination due to its ability to lower systolic and diastolic blood pressure effectively. It helps in reducing the risks associated with chronic hypertension, such as heart disease and stroke.
Furthermore, amlodipine benazepril is particularly useful for patients who are not adequately controlled on monotherapy. The fixed-dose combination simplifies adherence, reducing pill burden. Additionally, it’s beneficial for patients with comorbid conditions such as diabetes, where blood pressure management is critical to prevent cardiovascular complications.
It is also indicated in patients experiencing side effects from other antihypertensive medications. By switching to amlodipine benazepril, healthcare providers can offer a well-tolerated option that provides substantial blood pressure control.
In cases of heart failure or ischemic heart disease, this combination may improve outcomes by addressing both blood pressure and cardiac workload. Regular monitoring of renal function and potassium levels is essential to ensure safety and effectiveness during treatment.
In summary, consider amlodipine benazepril for patients seeking improved hypertension management, especially when monotherapy falls short or when patients have additional health considerations. Adjustments in dosage may be necessary based on individual response and tolerance.
Dosage Guidelines and Administration Tips
The recommended starting dose of Amlodipine Benazepril for most adults is 5 mg/10 mg once daily. Depending on individual response, the dose may increase to a maximum of 10 mg/40 mg per day. Adjustments should be made cautiously to minimize potential side effects.
For patients with renal impairment, consider a lower starting dose to reduce the risk of adverse reactions. Monitor these patients closely when initiating therapy or adjusting dosage.
Take Amlodipine Benazepril at the same time each day to maintain consistent blood levels. This helps optimize the medication’s effectiveness. You can take it with or without food, providing flexibility in your daily routine.
Do not crush or chew the tablet; swallowing it whole ensures proper absorption. Stay hydrated while on this medication, as dehydration can lead to increased side effects.
Monitor blood pressure regularly to assess the medication’s effectiveness and adjust doses accordingly with guidance from your healthcare provider. If you miss a dose, take it as soon as you remember, unless it’s almost time for your next dose. In such cases, skip the missed dose to avoid doubling up.
Inform your doctor about all medications you are taking, including over-the-counter drugs, supplements, and herbal products, to prevent potential interactions. Regular follow-ups with your healthcare provider will help optimize your treatment plan and ensure your health remains a priority.
Potential Side Effects and Interactions to Monitor
Monitor for dizziness or lightheadedness, especially when first starting Amlodipine Benazepril. These symptoms may indicate low blood pressure, particularly upon standing. If such effects occur, advise gradual position changes and consider checking blood pressure regularly.
Common Side Effects
Patients may experience swelling in the ankles or feet, which could indicate fluid retention. Report any significant swelling to a healthcare provider. Fatigue and flushing are also possible; review how these symptoms affect daily activities.
Drug Interactions
Pay close attention to interactions with non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs), as they can diminish the antihypertensive effects of Amlodipine Benazepril. Additionally, monitor potassium levels if using potassium supplements or potassium-sparing diuretics to avoid hyperkalemia. Always consult your healthcare provider before adding new medications.
Patient Compliance and Lifestyle Considerations
Adhering to the prescribed regimen for Amlodipine Benazepril significantly enhances treatment outcomes for hypertension and cardiovascular conditions. Follow these practical tips to boost compliance:
- Set Reminders: Use alarms or mobile apps to remind you about medication times.
- Organize Medications: Utilize pillboxes to keep daily doses sorted and easy to access.
- Track Progress: Keep a diary to note blood pressure readings and any side effects after taking medication.
Dietary choices play a crucial role in managing blood pressure. Incorporate these practices into daily life:
- Limit Sodium Intake: Aim for no more than 2,300 mg of sodium per day. Gradually reduce processed foods and always check labels.
- Increase Potassium-Rich Foods: Bananas, sweet potatoes, and spinach help lower blood pressure. Aim for a balanced intake of fruits and vegetables.
- Hydrate: Drinking plenty of water assists in overall health. Aim for at least eight cups daily.
Incorporate physical activity into your routine:
- Exercise Regularly: Set a goal of at least 150 minutes of moderate aerobic activity each week, such as brisk walking or cycling.
- Include Strength Training: Engage in muscle-strengthening activities on two or more days a week.
Monitor stress levels regularly:
- Practice Relaxation Techniques: Activities like yoga, meditation, or deep-breathing exercises can effectively reduce stress.
- Stay Connected: Engage with supportive friends and family to help manage emotional well-being.
Regular check-ups with your healthcare provider ensure that your treatment plan stays on track. Discuss any challenges you face with medication or lifestyle adjustments. Your active participation plays a significant role in achieving the best health outcomes.