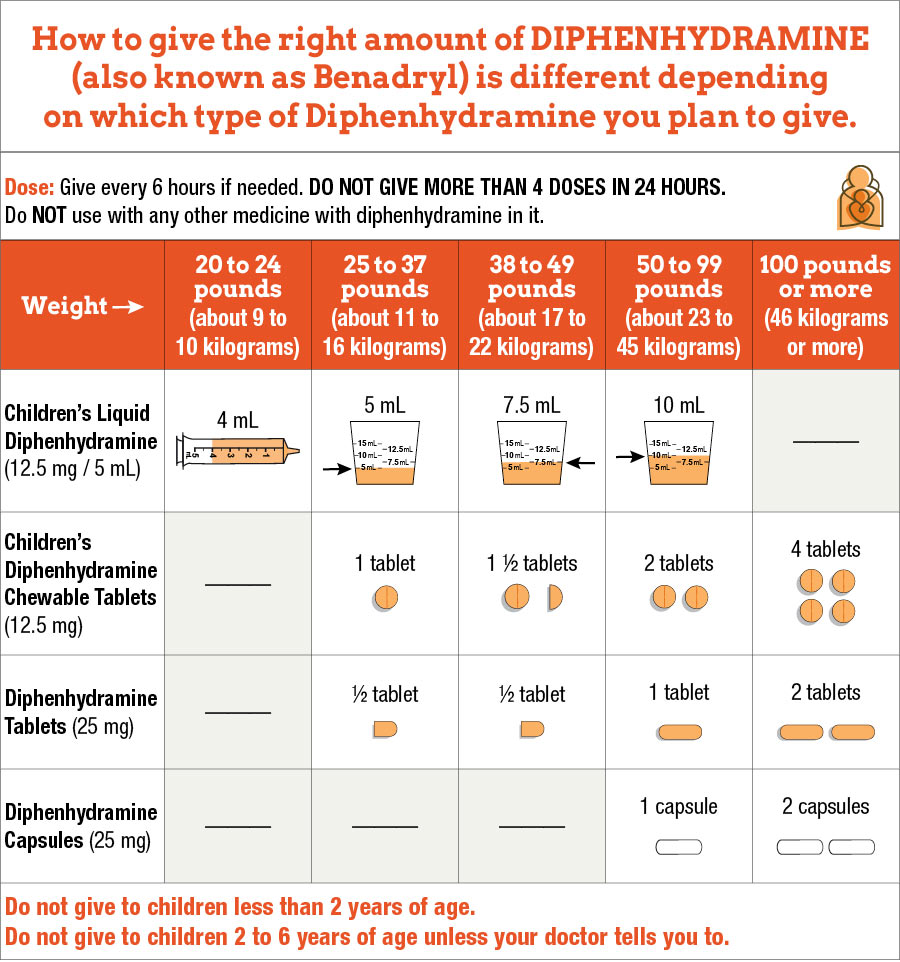
The recommended dose of Benadryl for most adults is 25 to 50 mg every four to six hours. It’s crucial not to exceed 300 mg in a 24-hour period. Finding the right dosage helps manage allergy symptoms effectively while minimizing potential side effects.
For optimal results, take Benadryl on an empty stomach with a full glass of water. This can enhance absorption and improve the medication’s efficacy. If you’re unsure about the right dosage for your specific situation, consulting a healthcare provider is advisable, especially if you have pre-existing conditions or are taking other medications.
If you experience drowsiness, consider adjusting the time you take the medication to avoid any disruption to your daily activities. Benadryl can significantly affect alertness, so planning accordingly helps maintain productivity. Always read the label or accompanying patient information leaflet for additional details on usage and warnings.
- Benadryl Dosage for Adults
- Considerations for Use
- Potential Side Effects
- Understanding Benadryl: Active Ingredients and Uses
- Recommended Dosage Guidelines for Adults
- Dosage for Allergic Reactions
- Dosage for Sleep Aid
- Factors Affecting Benadryl Dosage: Age, Weight, and Health Conditions
- Age
- Weight
- Health Conditions
- Possible Side Effects of Benadryl at Different Dosages
- When to Seek Medical Advice Regarding Benadryl Usage
- Alternatives to Benadryl: Other Antihistamines and Treatments
Benadryl Dosage for Adults
The standard dose of Benadryl (diphenhydramine) for adults is 25 to 50 mg every four to six hours as needed. Do not exceed 300 mg in 24 hours. It’s best to start with the lowest effective dose to minimize side effects, especially drowsiness.
Considerations for Use
If you are taking Benadryl for allergies, ensure you assess symptoms before re-dosing. Always consult with a healthcare professional if you have underlying conditions or are taking other medications. Pregnant or breastfeeding women should seek advice before using Benadryl.
Potential Side Effects
Common side effects include sedation, dry mouth, dizziness, and blurred vision. If you experience severe reactions, such as difficulty breathing or swelling, seek immediate medical attention. Adjust your dosage according to your body’s response, and avoid activities that require mental alertness until you know how Benadryl affects you.
Understanding Benadryl: Active Ingredients and Uses
Benadryl contains diphenhydramine, an antihistamine that effectively alleviates allergy symptoms like sneezing, runny nose, and itching. It also helps reduce symptoms of hay fever and other upper respiratory allergies.
In addition to its allergy relief properties, diphenhydramine acts as a sedative, making it useful for treating sleeplessness. Dosage should be tailored to individual needs, with a common recommendation for adults being 25-50 mg taken at bedtime for sleep support.
Benadryl can also be effective in managing symptoms of motion sickness, such as nausea and dizziness. For this purpose, adults may take 25-50 mg approximately 30 minutes before travel.
Other uses of diphenhydramine include:
- Mitigating reactions to insect bites or stings.
- Addressing symptoms of the common cold.
- Assisting in the management of certain types of Parkinson’s disease symptoms.
Be aware of potential side effects like drowsiness, dry mouth, and dizziness. Always consider these when determining your activities after taking Benadryl. Consult with a healthcare provider for personalized advice, especially if you are pregnant, breastfeeding, or managing other medications.
Recommended Dosage Guidelines for Adults
For adult individuals, the recommended dosage of Benadryl (Diphenhydramine) typically falls within the range of 25 to 50 mg every 4 to 6 hours, depending on the severity of symptoms. Avoid exceeding 300 mg in a 24-hour period. Always adhere to the labeling instructions unless directed otherwise by a healthcare professional.
Dosage for Allergic Reactions
In cases of allergic reactions, start with 25 to 50 mg taken orally. Monitor for relief of symptoms and adjust as necessary. Do not exceed the daily limit of 300 mg.
Dosage for Sleep Aid
When using Benadryl as a sleep aid, a dosage of 50 mg is commonly used about 30 minutes before bedtime. This should likewise not exceed 50 mg in a single dose and follow the daily limit.
| Use Case | Recommended Dosage | Maximum Daily Limit |
|---|---|---|
| Allergic Reactions | 25-50 mg every 4-6 hours | 300 mg |
| Sleep Aid | 50 mg before bedtime | 50 mg (single dose) |
Consult with a healthcare provider if you have pre-existing conditions, are taking other medications, or if symptoms persist beyond a few days. Always follow a professional’s advice for personalized guidance.
Factors Affecting Benadryl Dosage: Age, Weight, and Health Conditions
Benadryl dosage for adults varies based on several critical factors, including age, weight, and existing health conditions. Understanding these elements helps ensure safe and effective use of the medication.
Age
Age significantly influences Benadryl dosage. For older adults, the recommended dose may be lower due to metabolism changes and increased sensitivity to antihistamines. Typically, starting with 25 mg to 50 mg is advisable, taken every four to six hours as needed, while monitoring for side effects.
Weight
Weight also plays a crucial role in determining the appropriate dose. For those weighing less than average, a lower initial dosage may be more suitable. Standard dosing usually ranges from 25 mg to 50 mg per dose. However, individuals under 110 pounds might find that starting with 25 mg helps gauge their tolerance before increasing the dosage.
Health Conditions
- Existing Medical Conditions: Individuals with certain conditions, such as glaucoma, prostate issues, or respiratory problems, may require dosage adjustments or should consult a healthcare professional before use.
- Medications: Interactions with other medications can impact the safety and effectiveness of Benadryl. Always discuss current medications with a healthcare provider.
- Pregnancy and Breastfeeding: Consult a physician regarding safe usage during pregnancy or while breastfeeding, as dosages may differ.
Adjusting Benadryl dosage according to age, weight, and health status ensures safer and more effective relief from allergy symptoms. Regularly consult with a healthcare professional for personalized recommendations.
Possible Side Effects of Benadryl at Different Dosages
At lower dosages, such as 25 mg, Benadryl commonly causes drowsiness. This sedative effect may help individuals struggling with sleep or severe allergies. However, it can also lead to dizziness and dry mouth. Users should remain cautious if they plan to drive or operate heavy machinery.
When increasing the dosage to 50 mg, the likelihood of side effects escalates. Besides intensified drowsiness, users may experience confusion, and coordination issues. These symptoms are particularly concerning for older adults, who may be more sensitive to higher doses.
Doses exceeding 50 mg can lead to more severe reactions. Anticholinergic effects become pronounced, leading to urinary retention, constipation, and blurred vision. Some individuals may also experience increased heart rate or temperature fluctuations. Monitoring for these symptoms is crucial, especially in individuals with pre-existing conditions.
Long-term use or excessive dosages may lead to potential cognitive decline and increased risk of dementia in older adults. Users are advised to consult healthcare professionals before making any significant changes to dosage or duration of use.
Always listen to your body and consider the potential side effects when taking Benadryl. Adjusting dosages should be done judiciously to minimize unwanted reactions.
When to Seek Medical Advice Regarding Benadryl Usage
Consult a healthcare professional if you experience severe side effects, such as trouble breathing, swelling of the face or throat, or a rapid heartbeat after taking Benadryl. These symptoms may indicate an allergic reaction.
If your allergy symptoms do not improve after a few days of using Benadryl, reach out to your doctor for an alternative treatment plan. Extended use without improvement may require a reassessment of your condition.
Discuss with a physician if you are pregnant, nursing, or planning to become pregnant before using Benadryl, as it can pose risks to both the mother and baby.
Patients with pre-existing conditions like glaucoma, prostate enlargement, or respiratory issues should consult their healthcare provider to avoid complications. Benadryl can exacerbate these conditions.
Seek advice before mixing Benadryl with other medications, especially sedatives or alcohol, as this can increase drowsiness and lead to dangerous situations.
If you take high doses for extended periods, checking in with your doctor is wise. Prolonged usage can lead to dependency or other health issues.
Always reach out for guidance if unsure about your dosage or how the medication affects you. Better safe than sorry when it comes to your health.
Alternatives to Benadryl: Other Antihistamines and Treatments
Consider using cetirizine (Zyrtec) or loratadine (Claritin) as alternatives to Benadryl. Both antihistamines are less sedating, making them suitable for daytime use while effectively relieving allergy symptoms. Adults typically take cetirizine at 10 mg once daily or loratadine at 10 mg once daily.
Fexofenadine (Allegra) is another option, particularly for those who prefer a non-drowsy formula. It works well for seasonal allergies, with a standard dose of 180 mg once daily. It’s essential to stay hydrated, as this can enhance its effectiveness.
In cases where antihistamines are insufficient, nasal corticosteroids like fluticasone (Flonase) or mometasone (Nasonex) can provide targeted relief for nasal symptoms. Daily usage typically yields the best results, with the common recommendation being one or two sprays per nostril once daily.
For those with severe allergic reactions, epinephrine auto-injectors (such as EpiPen) are vital. Train yourself on how to use these injectors properly and keep them accessible if you have a history of significant allergic responses.
Natural alternatives also exist. Quercetin, a flavonoid found in many fruits and vegetables, may help stabilize mast cells and prevent histamine release. Dosages often range from 500 to 1000 mg daily, but consult a healthcare provider before starting any supplement.
Discuss these alternatives with a healthcare professional to identify the best approach tailored to your needs and symptoms.