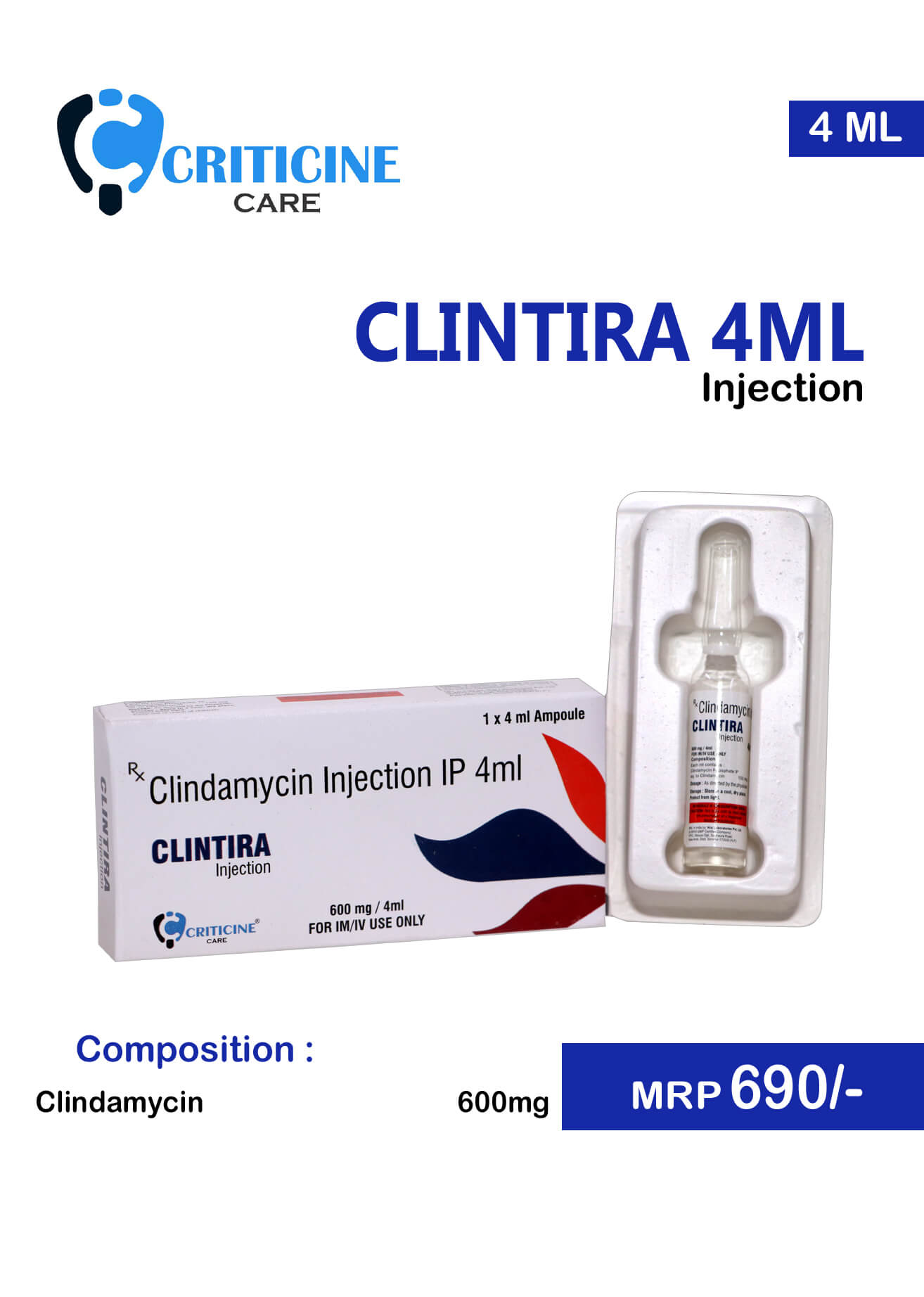
For managing serious bacterial infections, Clindamycin 600 mg intramuscular injection provides a reliable and potent option. This antibiotic works by inhibiting bacterial protein synthesis, effectively combating a range of Gram-positive bacteria. When prescribed by a healthcare professional, this form of medication is particularly useful in treating skin infections, respiratory infections, and infections of the bones and joints.
Before administration, it is essential to assess the patient’s medical history for potential allergies or contraindications. Clindamycin can cause gastrointestinal side effects, including diarrhea, which may indicate a more serious condition like Clostridium difficile colitis. Monitoring the patient after the injection helps mitigate risks and ensures a positive therapeutic outcome.
Proper injection technique enhances the medication’s effectiveness. The site should be chosen carefully, usually the gluteal muscle for IM injections, and the area must be sterilized to prevent infection. After the injection, watch for any immediate reactions, and provide post-injection care to support the healing process and maintain patient comfort.
- Clindamycin 600 mg IM Injection
- Indications and Uses of Clindamycin 600 mg IM Injection
- Specific Conditions Treated
- Usage Guidelines
- Administration Guidelines and Dosage for Clindamycin 600 mg IM Injection
- Dosage Recommendations
- Administration Steps
- Potential Side Effects and Interactions of Clindamycin 600 mg IM Injection
Clindamycin 600 mg IM Injection
Clindamycin 600 mg IM injection is indicated for the treatment of certain bacterial infections. This formulation is particularly effective against anaerobic bacteria and some protozoa. Administer this injection intramuscularly, ensuring proper aseptic technique to minimize the risk of infection.
Before administration, verify the patient’s allergy history, specifically to clindamycin or lincomycin. Monitor for signs of hypersensitivity during and after the injection. Assess the injection site for any adverse reactions, such as redness or swelling, which may indicate tissue irritation.
The dosage may vary based on the severity of the infection and patient response. It is crucial to adhere to recommended guidelines. Most adults typically receive 600 mg every 6 to 8 hours, but adjust dosage for specific clinical scenarios as necessary. For severe infections, higher doses might be considered under medical supervision.
Keep the patient well-hydrated throughout treatment. Encourage them to report any unusual symptoms, such as gastrointestinal disturbances or skin rashes. Regularly evaluate the patient’s progress, adjusting the treatment plan based on their response and any laboratory results that may guide therapy.
In cases of renal impairment, dose adjustment may be necessary. Consult current clinical guidelines for recommendations specific to such patients. Always review drug interactions, especially with other antibiotics or medications that may enhance the risk of side effects.
Clindamycin may disrupt the normal intestinal flora, leading to Clostridium difficile-associated diarrhea. Educate patients about the signs of colitis, such as severe abdominal pain or persistent diarrhea. If these symptoms arise, discontinue the medication and seek immediate medical advice.
Store clindamycin properly, keeping it away from light and heat. Inspect the solution for any discoloration or particulate matter before administration. If any abnormalities are present, discard the vial and use a new one.
Indications and Uses of Clindamycin 600 mg IM Injection
Clindamycin 600 mg intramuscular injection is recommended for treating serious infections caused by susceptible strains of anaerobic bacteria, as well as certain gram-positive bacteria. Clinicians commonly utilize this medication for skin and soft tissue infections, bone and joint infections, and intra-abdominal infections. It acts by inhibiting bacterial protein synthesis, effectively halting the growth of bacteria.
Specific Conditions Treated
This injection is especially useful in cases of osteomyelitis, a bone infection, and in patients with diabetic foot infections. Clindamycin is often chosen for its efficacy against certain strains of Streptococcus and Staphylococcus, including methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus (MRSA) in some instances. Additionally, it serves as an alternative for patients allergic to penicillin.
Usage Guidelines
Before administering Clindamycin, assess the patient for any history of gastrointestinal disorders, as it could cause colitis. Monitor liver and kidney function throughout treatment. Always consult a healthcare professional to determine the appropriate dosage and duration based on the infection severity and patient response.
By integrating Clindamycin 600 mg IM injection into treatment plans, healthcare providers can effectively manage and control serious bacterial infections, contributing to enhanced patient outcomes.
Administration Guidelines and Dosage for Clindamycin 600 mg IM Injection
Administer Clindamycin 600 mg via intramuscular (IM) injection in the muscle of the upper outer quadrant of the buttock or the vastus lateralis of the thigh. Ensure proper aseptic technique throughout the procedure to minimize infection risk.
Dosage Recommendations
The recommended dosage for adults and pediatric patients over 16 years of age is typically 600 mg every 6 to 8 hours, depending on the severity of the infection. For pediatric patients aged 1 month to 16 years, dosing is generally based on weight. Calculate the initial dose as 10 to 25 mg/kg/day, divided into two to four doses.
Administration Steps
- Prepare the injection site by cleansing with an appropriate antiseptic solution.
- Use a sterile syringe and needle suitable for IM injection (typically 21-23 gauge).
- Withdraw the Clindamycin solution and expel any air bubbles.
- Insert the needle at a 90-degree angle to the skin, inject the medication slowly, and withdraw the needle after injection.
- Apply gentle pressure to the site with a sterile cotton ball or gauze.
Monitor the patient for any adverse reactions post-injection, including but not limited to pain, swelling, or allergic reactions. Adjust dosing based on the clinical response and observed side effects to ensure patient safety and therapeutic effectiveness.
Potential Side Effects and Interactions of Clindamycin 600 mg IM Injection
Clindamycin 600 mg intramuscular injection can lead to specific side effects, including gastrointestinal disturbances such as diarrhea, nausea, and vomiting. Patients should monitor for signs of Clostridium difficile-associated diarrhea, which can occur during or after treatment. Allergic reactions are possible; symptoms may include rash, itching, or difficulty breathing. If severe reactions occur, seek immediate medical attention.
Local reactions at the injection site may arise, often presenting as redness or swelling. Staying aware of these reactions will help in identifying potential complications. Liver function tests should be considered for patients with liver issues as Clindamycin is metabolized in the liver, increasing the risk of liver toxicity.
Drug interactions pose another concern. Clindamycin can antagonize the effects of certain antibiotics, particularly those targeting gram-positive organisms. Combining it with neuromuscular blocking agents may enhance muscle relaxation effects, heightening respiratory risks. Always inform healthcare providers of all medications being taken to prevent adverse interactions.
Pregnant and breastfeeding individuals should consult healthcare providers, as the use of Clindamycin during these periods carries some risks. Proper assessment before administration can support safer treatment decisions.
Regular monitoring and communication with healthcare professionals ensure effective management of potential side effects and interactions. Being proactive in these conversations can help identify and mitigate any concerns that may arise during treatment with Clindamycin. Always prioritize safety and wellness throughout the treatment process.