Clomid can significantly impact menstrual cycles, especially when periods are absent or irregular. Women considering Clomid should consult with a healthcare provider to assess whether their short menstrual cycles are a symptom of underlying reproductive health issues. This medication is commonly used to stimulate ovulation in women who have difficulty conceiving.
When Clomid is prescribed, it often leads to adjustments in a woman’s hormonal balance, which may result in shorter periods or changes in flow. Monitoring these changes can help determine the medication’s effectiveness. Regular check-ups with a healthcare professional can provide guidance on managing these side effects and optimizing fertility treatment.
For those experiencing unusually short periods while on Clomid, it’s crucial to document any changes in cycle regularity and flow. This information can help identify patterns and inform discussions with a healthcare provider regarding ongoing treatment strategies. Understanding these dynamics ensures a tailored approach to fertility management.
- Clomid and Short Period: A Comprehensive Overview
- Understanding Clomid’s Impact on Menstrual Cycle
- Managing Short Periods While on Clomid
- Understanding Clomid and Its Mechanism of Action
- Impact of Clomid on Menstrual Cycle Duration
- When to Consult a Healthcare Professional About Short Periods
- Alternative Treatments for Irregular Menstrual Cycles
- Dietary Adjustments
- Physical Activity
Clomid and Short Period: A Comprehensive Overview
Clomid can lead to changes in menstrual cycles for some users, including shorter periods. If you notice your periods becoming noticeably shorter while taking Clomid, consult with your healthcare provider for personalized advice and assessment.
Understanding Clomid’s Impact on Menstrual Cycle
Clomid, or clomiphene citrate, is widely used for stimulating ovulation. As it alters hormonal levels, some users may experience variations in their menstrual cycle. Shorter periods may occur due to the medication’s influence on estrogen levels, affecting the uterine lining. Monitoring your cycle while taking Clomid is crucial, as any significant changes could signal the need for an evaluation.
Managing Short Periods While on Clomid
If shorter periods arise, keep a detailed record of your menstrual cycles, noting any additional symptoms such as changes in flow or duration. This information aids healthcare providers in tailoring your treatment. In some cases, additional hormonal assessments may be required to ensure Clomid is optimizing ovulation without compromising menstrual health.
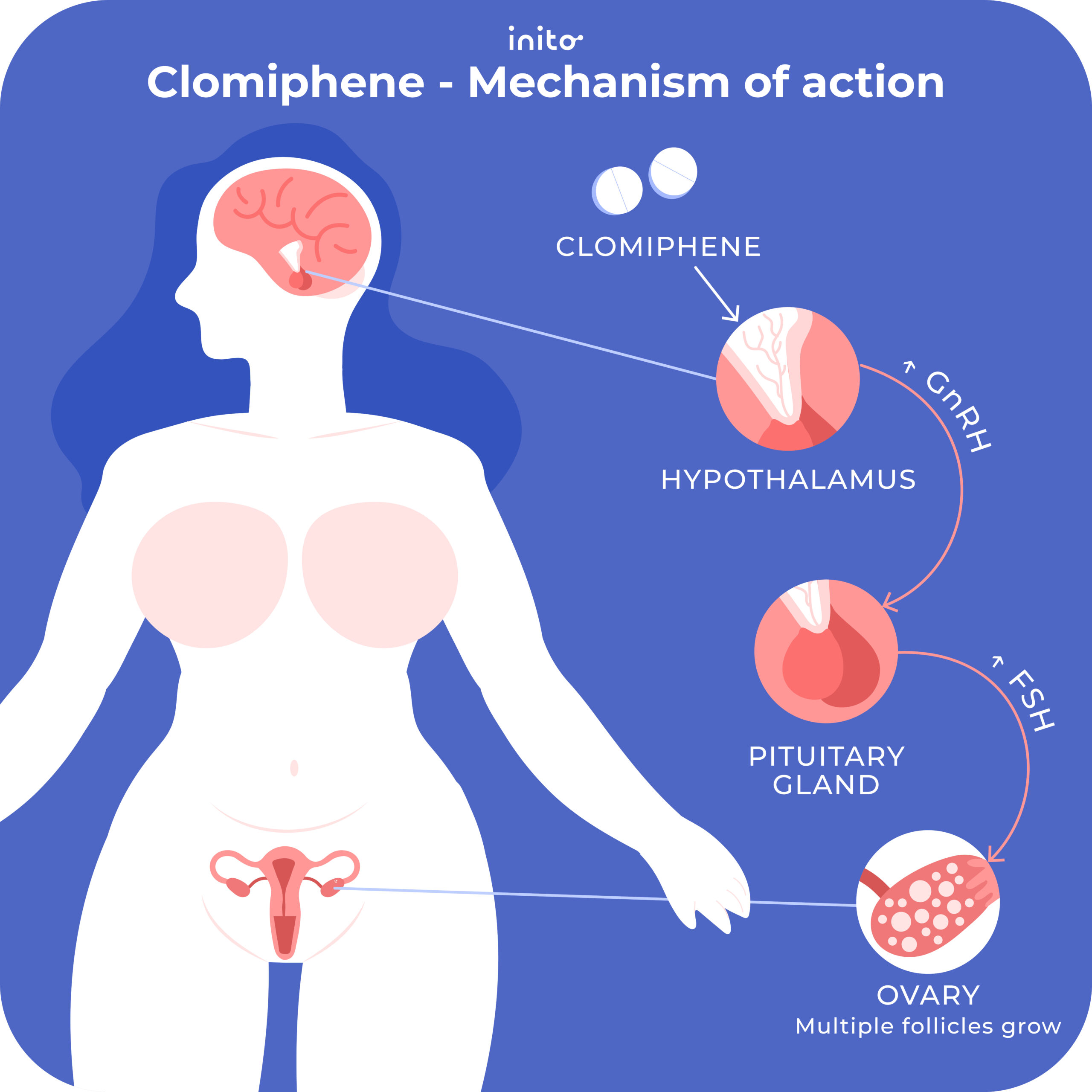
Understanding Clomid and Its Mechanism of Action
Clomid, or Clomiphene Citrate, is widely used to treat female infertility, particularly in women with irregular ovulation. It works primarily as a selective estrogen receptor modulator (SERM). By binding to estrogen receptors in the hypothalamus, Clomid blocks the effects of estrogen, leading to an increase in gonadotropin-releasing hormone (GnRH) release. This cascade effect stimulates the pituitary gland to produce more follicle-stimulating hormone (FSH) and luteinizing hormone (LH), promoting ovarian function and ovulation.
When beginning treatment with Clomid, doctors typically prescribe a dose of 50 mg per day for five days, starting on the fifth day of the menstrual cycle. This dosage may be adjusted based on the patient’s response. Monitoring through ultrasound can track follicle development, ensuring that ovulation occurs. Patients should remain observant for side effects, such as hot flashes or mood swings, which are relatively common.
Research shows that Clomid is effective in inducing ovulation in 70-80% of women who use it correctly. For those who do not achieve pregnancy after several cycles, alternative options may be explored, including other medications or assisted reproductive technologies.
Overall, understanding how Clomid affects the hormonal pathways in the body can help patients optimize their treatment and increase their chances of conception. Regular communication with healthcare providers throughout the treatment process ensures tailored care and support.
Impact of Clomid on Menstrual Cycle Duration
Clomid can lead to variations in menstrual cycle duration. Typically, this medication stimulates ovulation in women experiencing irregular cycles, which may alter the timing and length of periods.
Users may notice the following effects:
- Lengthened Cycles: Some women experience longer cycles as Clomid influences hormone levels and ovulation timing.
- Shortened Cycles: Others may find their cycles shortened, particularly if they respond rapidly to the medication.
- Irregular Patterns: Clomid can cause fluctuations in cycle length, resulting in unpredictability for some users.
It’s crucial to monitor your cycles while on Clomid. Keeping a menstrual diary can help track these changes and allow for better communication with your healthcare provider.
Consult your doctor if your menstrual cycles become significantly longer or shorter than your typical pattern while using Clomid. Adjustments to dosage or alternative treatments may be necessary for your specific situation.
Each individual’s response to Clomid is unique. Regular follow-ups can help to understand how this medication interacts with your body and ensure that your reproductive health remains a priority.
When to Consult a Healthcare Professional About Short Periods
Consult a healthcare professional if your menstrual cycle consistently lasts less than 21 days. Short periods may indicate hormonal imbalances or other underlying health issues that require attention.
If you experience sudden changes in your cycle pattern, such as a significant decrease in flow or duration, do not hesitate to seek medical advice. These changes can signal conditions like polycystic ovary syndrome (PCOS) or thyroid disorders.
Experiencing unusual symptoms alongside short periods, such as severe pain, excessive fatigue, or unusual discharge, warrants a consultation. These may suggest infections or other conditions that need prompt intervention.
Women trying to conceive should also consult a healthcare provider if their cycles are short. Understanding ovulation patterns is critical for fertility, and a shortened cycle may affect conception chances.
Lastly, if you are taking Clomid and notice changes in your menstrual cycle, contact your doctor. They can help assess whether the medication is effective or if adjustments are necessary.
Alternative Treatments for Irregular Menstrual Cycles
Consider acupuncture as a method to help regulate your menstrual cycle. Research indicates that acupuncture may improve blood flow to the reproductive organs and balance hormone levels. Regular sessions can be beneficial for those experiencing irregular cycles.
Herbal remedies, such as chaste tree berry (Vitex agnus-castus), can promote hormonal balance. Studies show that this herb helps to alleviate symptoms of premenstrual syndrome (PMS) and may support a more consistent cycle. Always consult a healthcare provider before starting any herbal treatment.
Dietary Adjustments
Nutrition plays a significant role in regulating menstrual cycles. Incorporate foods rich in omega-3 fatty acids, such as fish, walnuts, and flaxseeds. These foods support hormonal balance. Additionally, maintain a diet high in whole grains, fruits, and vegetables to promote overall health and regularity.
Physical Activity
Regular exercise contributes positively to menstrual health. Aim for a mix of cardiovascular activities and strength training. Activities like yoga or Pilates can reduce stress, which often influences cycle irregularities. Create a balanced fitness routine that fits your lifestyle.
| Method | Benefits |
|---|---|
| Acupuncture | Improves blood flow and balances hormones |
| Chaste Tree Berry | Promotes hormonal balance; alleviates PMS |
| Dietary Changes | Supports overall health and regular cycles |
| Regular Exercise | Reduces stress; improves menstrual health |
Tracking your cycle with a calendar or an app can provide valuable insights. By noting patterns and symptoms, you can better understand your body and discuss any irregularities with your healthcare provider. This information will help tailor a treatment plan that works for you.