Clomid (clomiphene citrate) is known for its role in stimulating ovulation, but many wonder about its impact on cervical mucus. Research indicates that some users may experience reduced cervical mucus production while on Clomid, which could influence fertility. If you’re considering Clomid or are currently prescribed it, understanding this aspect is crucial for optimizing your chances of conception.
Cervical mucus plays a vital role in fertility, as it facilitates sperm movement and survival. A decrease in quality or quantity of cervical mucus can hinder this process. It’s essential to monitor any changes closely after starting Clomid. Consulting with a healthcare provider about these effects can provide personalized guidance and alternate options to support cervical mucus production.
To enhance cervical mucus during Clomid treatment, consider staying well-hydrated and incorporating fertility-friendly foods such as healthy fats and whole grains into your diet. Certain supplements, like vitamin E or evening primrose oil, may also support mucus production, but always discuss these additions with your doctor first. Taking proactive steps can maximize your fertility journey while using Clomid.
- Does Clomid Dry Up Cervical Mucus?
- Understanding Clomid and Its Function
- Mechanism of Action
- Cervical Mucus and Clomid
- How Clomid Affects Hormone Levels
- The Role of Cervical Mucus in Fertility
- Research on Clomid and Cervical Mucus
- Symptoms of Dry Cervical Mucus Due to Clomid
- Strategies to Manage Cervical Mucus Changes
- Hydration Matters
- Dietary Adjustments
- Natural Supplements
- Timing in Your Cycle
- Consult a Specialist
- Consulting Your Healthcare Provider About Clomid
Does Clomid Dry Up Cervical Mucus?
Clomid may lead to decreased cervical mucus in some women. This side effect occurs because Clomid works by blocking estrogen receptors, which can impact the production of cervical mucus. When cervical mucus is insufficient, it can interfere with sperm motility and ultimately affect fertility.
Monitoring changes in cervical mucus is essential while taking Clomid. Women often notice changes in texture and quantity. Ideally, fertile cervical mucus appears clear, stretchy, and similar to egg whites. If you observe a significant decrease in mucus, it’s helpful to communicate this with your healthcare provider.
In cases where Clomid contributes to reduced mucus, alternative strategies can help. Staying well-hydrated is crucial, as it can improve overall bodily functions, including mucus production. Additionally, some women find that using fertility-friendly lubricants can create a more conducive environment for sperm movement. Herbal remedies and supplements may also be explored, but consulting a healthcare professional before trying these options is advisable.
Ultimately, if decreased cervical mucus is a concern while taking Clomid, discussing it with your fertility specialist can lead to tailored solutions or adjustments in your treatment plan. Tracking your body’s signals provides valuable information to optimize your fertility journey.
Understanding Clomid and Its Function
Clomid, or clomiphene citrate, primarily stimulates ovulation by impacting the hormonal regulation within the body. It effectively blocks estrogen receptors in the hypothalamus, leading to an increased release of hormones that promote ovulation. This medication is often prescribed for women dealing with polycystic ovary syndrome (PCOS) or other fertility issues where ovulation may be irregular or absent.
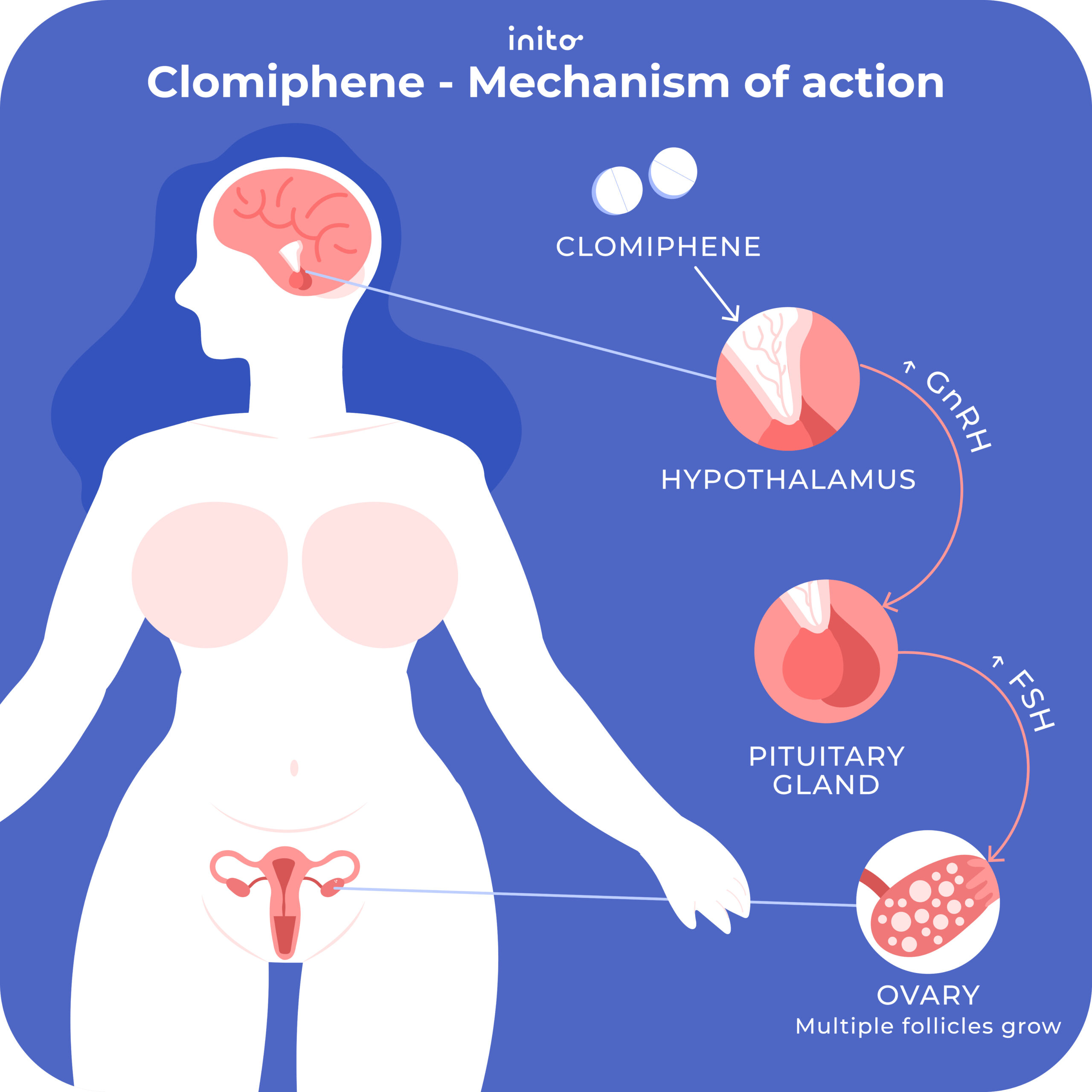
Mechanism of Action
When Clomid is taken, it encourages the pituitary gland to release more follicle-stimulating hormone (FSH) and luteinizing hormone (LH). These hormones play critical roles in maturing ovarian follicles and triggering ovulation. By enhancing the body’s natural hormonal environment, Clomid aims to create conditions conducive to conception.
Cervical Mucus and Clomid
Some users report concerns regarding cervical mucus when using Clomid. While Clomid can influence cervical mucus production, research indicates that not all women experience a significant reduction. In some cases, cervical mucus may become less hospitable due to hormonal changes spurred by Clomid. It’s advisable to monitor cervical mucus during treatment, as fertile mucus is crucial for sperm mobility and survival. If issues arise, consulting with a healthcare provider can lead to tailored solutions.
How Clomid Affects Hormone Levels
Clomid primarily influences estrogen and progesterone levels in the body. By blocking estrogen receptors in the hypothalamus, Clomid tricks the body into thinking estrogen levels are low. This stimulates the release of gonadotropin-releasing hormone (GnRH), followed by increased production of follicle-stimulating hormone (FSH) and luteinizing hormone (LH).
As a result, Clomid directly affects the ovaries, promoting the development of ovarian follicles and encouraging ovulation. Monitoring hormone levels during treatment can provide insights into how effectively Clomid is working. Regular blood tests can reveal FSH and LH levels, offering a clear picture of ovarian response.
Some individuals might experience fluctuations in progesterone levels after ovulation, which is crucial for maintaining a healthy pregnancy if conception occurs. Understanding these levels helps in assessing the potential for successful ovulation and pregnancy outcomes.
Clomid may also impact cervical mucus production. While its primary function is to stimulate ovulation, changes in hormone levels can affect mucus consistency, potentially leading to drier cervical mucus. It’s advisable to track changes in mucus quality, as this can signify the optimal timing for conception.
For anyone considering Clomid, consulting with a healthcare provider is vital. Reviewing hormone levels and any side effects, including changes in cervical mucus, ensures tailored advice and support during treatment.
The Role of Cervical Mucus in Fertility
Cervical mucus plays a pivotal role in enhancing fertility. It acts as a natural barrier that helps sperm navigate through the cervix into the uterus. During ovulation, the quality and quantity of cervical mucus improve, becoming stretchy and clear, similar to raw egg whites. This ideal consistency facilitates sperm movement, increasing the chances of successful fertilization.
To optimize cervical mucus production, stay well-hydrated and consume a balanced diet rich in fruits, vegetables, and omega-3 fatty acids. Regular exercise also promotes healthy circulation, which can positively impact mucus production. Monitor your menstrual cycle to identify ovulation timing, as this is when cervical mucus is at its peak.
Some women find that certain supplements, such as evening primrose oil or guaifenesin, may enhance cervical mucus quality. However, consult with a healthcare provider before starting any supplement regimen. Tracking changes in your mucus can provide insights into your fertile window, helping you strategically plan for conception.
In cases where medications like Clomid are used, some women may notice changes in cervical mucus. It is beneficial to discuss any concerns with a healthcare provider to understand how to manage these effects while trying to conceive.
Research on Clomid and Cervical Mucus
Clomid can influence cervical mucus production. Studies show varying results, with some women experiencing reduced mucus while taking the medication. This can impact fertility, as adequate cervical mucus is essential for sperm transport.
- Research indicates that Clomid may lead to dry cervical mucus in some cases.
- It’s essential to monitor changes in cervical mucus when starting Clomid, especially near ovulation.
- Some studies suggest using ovulation predictor kits for better timing if cervical mucus appears inadequate.
Women concerned about cervical mucus can consider the following approaches:
- Increase fluid intake to promote hydration and potentially improve mucus quality.
- Incorporate foods rich in omega-3 fatty acids to encourage mucus production.
- Consult a healthcare provider about alternatives or supplements that may support cervical mucus production.
Staying in touch with your doctor is crucial. Regular check-ins can help adjust treatment plans based on your specific response to Clomid and the condition of your cervical mucus.
In conclusion, observing any changes and addressing concerns proactively can enhance the overall fertility experience while using Clomid.
Symptoms of Dry Cervical Mucus Due to Clomid
Dry cervical mucus while using Clomid may manifest through several noticeable symptoms. Women often report a lack of lubrication during their menstrual cycle, especially around ovulation. This reduced mucus can lead to discomfort during intimacy.
Typical signs include:
| Symptom | Description |
|---|---|
| Increased vaginal dryness | During Clomid treatment, many experience a significant decrease in natural lubrication, which can lead to discomfort. |
| Changes in discharge | Mucus may appear thicker or less abundant, deviating from the usual patterns observed during ovulation. |
| Difficulty identifying ovulation | Some women may find it hard to recognize fertile days due to less noticeable cervical mucus. |
| Painful intercourse | A lack of moisture can result in friction and discomfort during sexual activities. |
If you notice these symptoms, discussing them with a healthcare provider is advisable. Adjustments to your treatment regimen may be necessary to alleviate the dryness and enhance comfort without compromising fertility goals.
Strategies to Manage Cervical Mucus Changes
Monitor your cervical mucus daily to identify patterns. Check for changes in consistency, color, and amount. Using a dedicated chart can help track cycles effectively.
Hydration Matters
Stay well-hydrated. Drinking plenty of water can thin mucus and potentially enhance its quality. Aim for at least 8 glasses a day to maintain optimal overall hydration.
Dietary Adjustments
Incorporate foods rich in vitamins C and E, along with omega-3 fatty acids. Consider adding:
- Citrus fruits
- Nuts and seeds
- Fatty fish
- Green leafy vegetables
Avoid excessive caffeine and alcohol, which might dehydrate the body and impact mucus production.
Natural Supplements
Explore natural supplements like evening primrose oil or fish oil. These can help improve cervical mucus quality, although consult with a healthcare provider before starting any new supplements.
Timing in Your Cycle
Understand your fertile window. Engage in intimacy during periods of abundant cervical mucus, typically occurring around ovulation. This can increase the chances of conception.
Consult a Specialist
If changes are significant or concerning, seek advice from a healthcare professional. They can evaluate hormone balance and suggest further interventions if necessary.
Implementing these strategies can help manage changes in cervical mucus and support reproductive health. Regular monitoring and healthy lifestyle choices work together to enhance your overall well-being.
Consulting Your Healthcare Provider About Clomid
Discuss your specific concerns regarding Clomid with your healthcare provider. Ask about its potential effects on cervical mucus, as alterations in mucus can impact fertility. Review your medical history to ensure Clomid is a suitable option for you.
Inquire about the monitoring process during treatment. Your doctor may suggest ultrasounds or blood tests to check your response to Clomid and track ovulation. Understanding how these assessments work allows you to prepare for each step.
Address any side effects you may experience or fear. Common reactions include mood swings, hot flashes, and abdominal discomfort. Knowing what to expect can alleviate anxiety about beginning treatment.
Evaluate the timeline of treatment with your practitioner. Discuss how long you will take Clomid and what the next steps will be if conception doesn’t occur. This clarity provides a roadmap moving forward.
Consider discussing lifestyle factors that may impact your fertility, including diet, exercise, and stress management. Your provider can offer tailored advice to support your overall health during this period.
Always feel empowered to ask questions. Clarifying doubts ensures you understand Clomid’s role and enhances your ability to make informed decisions about your reproductive health.