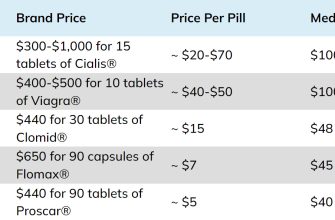
For those experiencing erectile dysfunction, vardenafil hydrochloride provides a targeted approach to restoring sexual health. This medication functions as a phosphodiesterase type 5 (PDE5) inhibitor, promoting increased blood flow to the penis when arousal occurs. By enhancing natural physiological responses, vardenafil offers a pathway to a satisfying intimate life.
It’s recommended to take vardenafil approximately 30 minutes before engaging in sexual activity. This timeframe allows the drug to reach optimal levels in the bloodstream. Patients typically benefit from vardenafil taken on an as-needed basis, with effects lasting for about four to five hours. Adherence to medical guidance ensures both safety and efficacy.
Consultation with a healthcare provider is advisable before starting vardenafil. A physician will assess individual health histories and current medications to determine suitability. Potential interactions with nitrates or other medications could pose risks, so thorough disclosure of all treatments is crucial.
Side effects such as headache, flushing, or nasal congestion are commonly reported but generally mild. Understanding these potential reactions helps users make informed decisions while considering vardenafil as a treatment option. Regular follow-ups with a healthcare professional allow for ongoing evaluation and adjustments as needed, ensuring the best outcome for your health.
Drug Prescription: Vardenafil Hydrochloride
Vardenafil hydrochloride is prescribed primarily for treating erectile dysfunction. Patients should take this medication approximately 30 minutes before sexual activity, benefiting from its effects for up to 5 hours. The recommended starting dose is typically 10 mg. Healthcare providers may adjust this dosage based on individual response and tolerability.
Administration Guidelines
Swallow the tablet whole with a glass of water; do not crush or chew it. Avoid taking vardenafil with high-fat meals as this may delay the onset of its action. Consumption of alcohol should be limited, as it can increase the risk of side effects. Discuss any other medications you are taking with your doctor to prevent potential interactions.
Possible Side Effects
Common side effects can include headaches, flushing, nasal congestion, and dizziness. If you experience severe reactions such as chest pain, sudden vision loss, or an erection lasting more than four hours, seek medical attention immediately. Your physician will evaluate the risks and benefits before prescribing this medication, ensuring it aligns with your health needs.
Pharmacological Properties and Mechanism of Action of Vardenafil
Vardenafil hydrochloride acts primarily as a selective phosphodiesterase type 5 (PDE5) inhibitor. It enhances erectile function by increasing blood flow to the penis during sexual stimulation. This action occurs through the inhibition of PDE5, which is responsible for the degradation of cyclic guanosine monophosphate (cGMP), a molecule that plays a key role in erectile physiology.
During sexual arousal, nitric oxide (NO) is released in the corpus cavernosum, stimulating the production of cGMP. Vardenafil not only prevents the breakdown of cGMP but also prolongs its effects. This results in smooth muscle relaxation and vasodilation, promoting increased blood inflow and facilitating an erection.
The pharmacokinetics of vardenafil highlight its rapid absorption, with peak plasma concentrations reached approximately 1 hour after oral administration. Its effects can last for up to 6 hours, allowing for a window of opportunity for sexual activity. Vardenafil demonstrates a favorable safety profile, with common side effects including headache, flushing, and nasal congestion.
Vardenafil is also well-tolerated in patients with other medical conditions such as hypertension or diabetes. However, caution is advised when used in combination with nitrates, as this could lead to significant hypotension. Evaluating patient history and concurrent medications is essential to optimize the therapeutic outcome.
In summary, vardenafil hydrochloride effectively enhances erectile function by blocking PDE5 activity and increasing cGMP levels in the corpus cavernosum, providing a reliable option for managing erectile dysfunction.
Indications, Dosage, and Administration Guidelines for Vardenafil
Vardenafil is primarily indicated for the treatment of erectile dysfunction in men. It helps achieve and maintain an erection sufficient for sexual activity.
Dosage recommendations typically include:
- Initial dose: 10 mg taken orally, about 30 to 60 minutes before sexual activity.
- Adjustable dose: May increase to 20 mg or decrease to 5 mg based on effectiveness and tolerability.
- Maximum frequency: Do not exceed once per day.
Administration guidelines are as follows:
- Avoid high-fat meals, which can delay the onset of action.
- Consult a healthcare provider for individuals with cardiac conditions.
- Take vardenafil as needed, not on a regular schedule unless directed by a healthcare professional.
Those with liver or kidney issues may require dose adjustments. Patients taking medications for hypertension or other conditions should discuss potential interactions with their healthcare provider.
For the best results, maintain open communication with your healthcare provider about any side effects or concerns regarding vardenafil usage.
Potential Side Effects and Contraindications of Vardenafil Use
Common side effects of vardenafil include headaches, flushing, nasal congestion, and dizziness. Patients may also experience upset stomach or altered vision, such as increased sensitivity to light. Mild back pain might occur as well. If these effects persist or worsen, consult a healthcare provider.
Serious side effects, while rare, may involve sudden vision loss or hearing impairment. Seek immediate medical attention if experiencing chest pain, shortness of breath, or irregular heartbeat. These symptoms might indicate severe cardiovascular complications.
Contraindications to vardenafil usage include pre-existing cardiovascular conditions, such as severe heart disease or recent heart attack. Patients taking nitrates for angina must avoid this medication, as the combination can lead to dangerous drops in blood pressure. Individuals with low blood pressure or severe liver impairment should also refrain from using vardenafil.
Men with certain anatomical conditions, like penile deformities or conditions that can increase the risk of priapism, should discuss these with their healthcare provider. Caution is advised for those taking other medications that influence blood pressure or sexual function.
Open communication with a healthcare provider ensures safe usage of vardenafil. Always report any concurrent medications or health issues to receive personalized guidance and support.