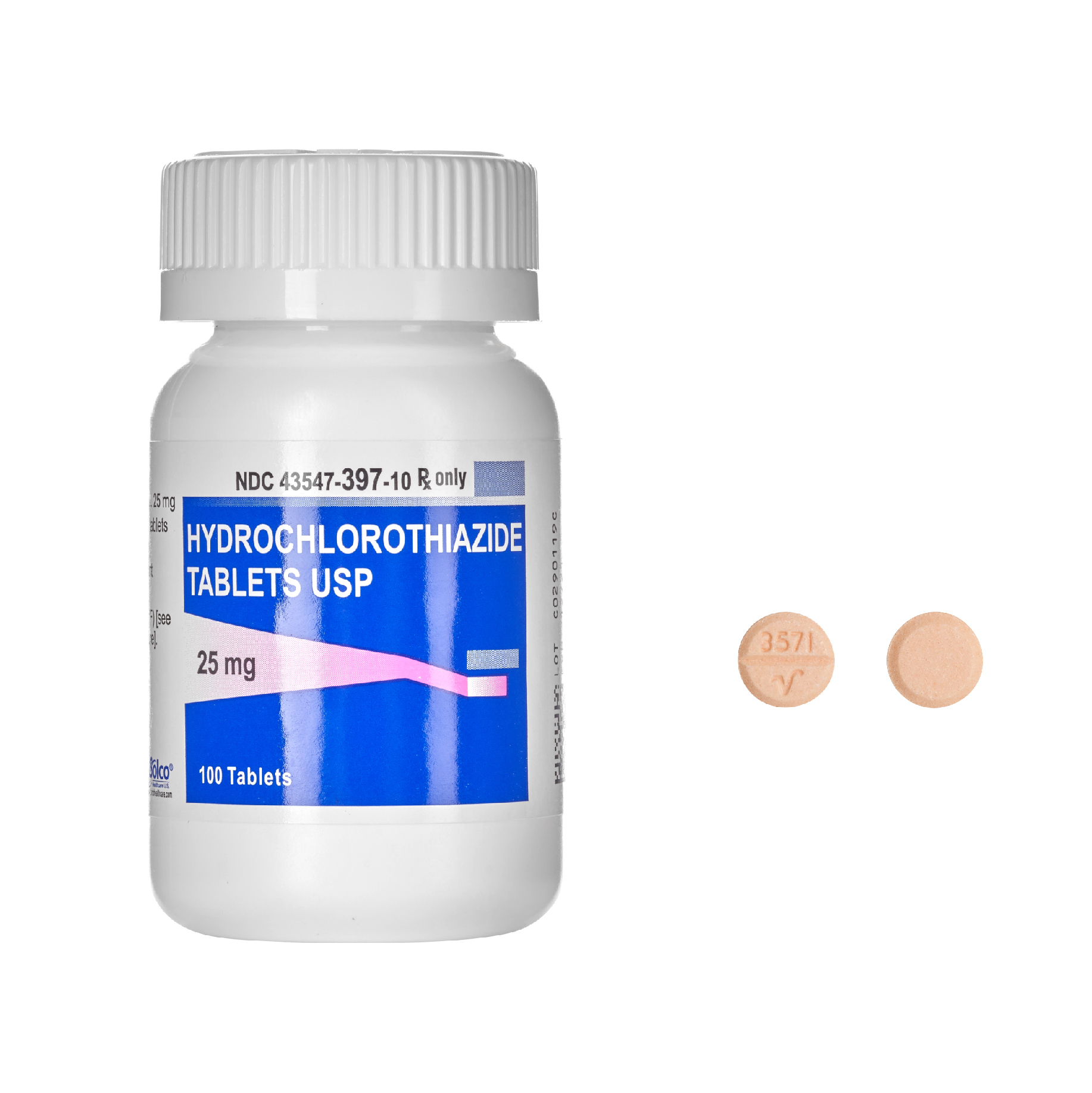
Hydrochlorothiazide is a generic medication primarily used to treat hypertension and edema. This thiazide diuretic works by promoting the removal of excess fluid and salt from the body, leading to lowered blood pressure and reduced swelling. Available under various brand names, hydrochlorothiazide remains a popular choice due to its affordability and efficacy.
Patients often benefit from hydrochlorothiazide because it not only helps in managing blood pressure but also aids in preventing complications like heart disease and stroke. It’s essential for users to adhere to their prescribed dosage, as this will ensure optimal results and minimize the risk of side effects.
In combination with lifestyle changes such as a balanced diet and regular exercise, hydrochlorothiazide can play a significant role in effective long-term hypertension management. When considering this medication, consulting with a healthcare provider allows for personalized treatment plans and monitoring for any potential interactions with other medications.
- Hydrochlorothiazide is Generic for
- Understanding Hydrochlorothiazide: Mechanism of Action
- Brand Names Commonly Associated with Hydrochlorothiazide
- Therapeutic Uses of Hydrochlorothiazide in Clinical Practice
- Dosage Forms and Administration Guidelines for Hydrochlorothiazide
- Recommended Dosage
- Administration Guidelines
- Side Effects and Contraindications of Hydrochlorothiazide
- Common Side Effects
- Serious Side Effects
- Contraindications
- Comparing Hydrochlorothiazide with Other Diuretics
- Mechanism of Action
- Side Effects and Monitoring
Hydrochlorothiazide is Generic for
Hydrochlorothiazide is a generic medication primarily used to manage high blood pressure and fluid retention. It belongs to a class of drugs known as thiazide diuretics, which help the body eliminate excess water and sodium through urine. This action effectively reduces blood pressure and decreases swelling.
Common brand names for hydrochlorothiazide include HydroDIURIL, Microzide, and Esidrix. While these brands contain the same active ingredient, hydrochlorothiazide operates by dilating blood vessels and increasing urine production, assisting in blood pressure control.
The standard doses of hydrochlorothiazide range from 12.5 mg to 50 mg per day, based on individual patient needs and response. Regular monitoring of blood pressure and electrolyte levels is essential during treatment.
| Brand Name | Dosage Forms | Indications |
|---|---|---|
| HydroDIURIL | Tablets | Hypertension, Edema |
| Microzide | Capsules | Hypertension, Edema |
| Esidrix | Tablets | Hypertension, Edema |
Hydrochlorothiazide can also be part of combination therapies, often paired with other antihypertensive agents for enhanced efficacy. Always consult healthcare providers to confirm the appropriateness of use and discuss potential interactions with other medications being taken.
Patient education on the importance of adherence to prescribed treatment and lifestyle modifications, such as diet and exercise, contributes positively to the management of hypertension and fluid retention.
Understanding Hydrochlorothiazide: Mechanism of Action
Hydrochlorothiazide primarily reduces blood pressure by inhibiting sodium reabsorption in the kidneys. It specifically acts on the distal convoluted tubule, blocking the sodium-chloride symporter. This results in increased excretion of sodium and chloride ions, leading to a decrease in blood volume.
The reduction in blood volume lowers the workload on the heart and dilates blood vessels, which helps reduce systemic vascular resistance. This dual action effectively contributes to lowering blood pressure and improving overall cardiovascular health.
Additionally, the diuretic effect helps prevent fluid retention, making hydrochlorothiazide useful in managing conditions like hypertension and edema. Its ability to promote diuresis also plays a role in alleviating heart failure symptoms and preventing complications related to high blood pressure.
Potential electrolyte imbalances can occur due to increased urination, particularly hypokalemia, which necessitates regular monitoring of potassium levels. Combining hydrochlorothiazide with potassium-sparing diuretics may counteract this effect.
Hydrochlorothiazide’s mechanism is underpinned by its ability to alter kidney function, making it a go-to option for healthcare providers treating hypertension and related conditions. Awareness of its action can enhance patient compliance and therapeutic outcomes.
Brand Names Commonly Associated with Hydrochlorothiazide
Hydrochlorothiazide has several brand names that are widely recognized. Here’s a list of some common names:
- Microzide: One of the most popular brand names for hydrochlorothiazide. It effectively manages high blood pressure and fluid retention.
- HydroDiuril: This brand is often prescribed for hypertension and edema, highlighting its diuretic effects.
- Esidrix: Known for treating high blood pressure, it also helps in reducing excess fluid.
- HCTZ: While
Therapeutic Uses of Hydrochlorothiazide in Clinical Practice
Hydrochlorothiazide primarily serves as a diuretic in the management of hypertension. By reducing blood volume, it effectively lowers arterial pressure, which can significantly decrease the risk of cardiovascular events.
This medication also addresses edema associated with congestive heart failure, cirrhosis, and renal disorders. Its ability to promote fluid excretion provides relief from swelling and discomfort in patients facing these conditions.
In patients with nephrolithiasis, hydrochlorothiazide can reduce the recurrence of calcium-containing kidney stones. It decreases calcium excretion in urine, helping to mitigate the formation of stones.
Additionally, hydrochlorothiazide plays a supportive role in treating diabetes insipidus, a condition characterized by excessive urination and thirst. The drug allows for better water retention and reduces urine output.
Regular monitoring of electrolytes is vital during hydrochlorothiazide therapy to avoid imbalances, especially hypokalemia. Adjusting dosages based on clinical response and side effects ensures optimal therapeutic outcomes for each patient.
Dosage Forms and Administration Guidelines for Hydrochlorothiazide
Hydrochlorothiazide is available primarily in oral tablet form, commonly in strengths of 12.5 mg, 25 mg, and 50 mg. The precise dosage depends on the specific condition being treated and individual patient needs.
Recommended Dosage
The initial dose for adults usually starts at 12.5 mg to 25 mg daily. For hypertension, the most commonly prescribed maintenance dose is 25 mg daily. In cases of edema, a higher dose, up to 50 mg daily, may be employed if necessary. Adjustments should be made based on the patient’s response and tolerance.
Administration Guidelines
Patients should take hydrochlorothiazide in the morning to minimize nocturia. It can be taken with or without food, but consistency is key for optimal results. Encourage hydration, as increased urination may lead to dehydration. Regular monitoring of blood pressure and electrolyte levels is recommended to ensure safety and efficacy.
Side Effects and Contraindications of Hydrochlorothiazide
Hydrochlorothiazide may cause a range of side effects. It’s crucial to monitor your response to the medication and discuss any unexpected symptoms with your healthcare provider.
Common Side Effects
- Increased urination
- Dizziness or lightheadedness
- Dry mouth
- Muscle cramps or weakness
- Headaches
- Fatigue
- Rash or itching
Serious Side Effects
- Severe allergic reactions (rash, itching, swelling)
- Jaundice (yellowing of the skin or eyes)
- Rapid heart rate or irregular heartbeat
- Signs of electrolyte imbalance (confusion, weakness, muscle pain)
Consult your doctor immediately if you experience any serious side effects. Regular monitoring of blood pressure and electrolytes is advised during treatment.
Contraindications
Hydrochlorothiazide is not suitable for everyone. Avoid this medication if you have:
- Severe kidney dysfunction
- Allergy to thiazide diuretics
- Low potassium levels (hypokalemia)
- Gout
- Active liver disease
Pregnant or breastfeeding individuals should discuss potential risks with their healthcare provider before starting hydrochlorothiazide. Always provide your doctor with a complete medical history to ensure safe use of this medication.
Comparing Hydrochlorothiazide with Other Diuretics
Hydrochlorothiazide (HCTZ) offers a unique set of benefits compared to other diuretics, particularly loop and potassium-sparing diuretics. Its ability to effectively reduce blood pressure while promoting sodium and water excretion makes it a preferred choice in treating hypertension and edema.
Mechanism of Action
HCTZ primarily works on the distal convoluted tubule in the kidneys, inhibiting sodium reabsorption. This leads to an increase in urinary excretion of sodium and water, resulting in reduced fluid volume in circulation. In contrast, loop diuretics like furosemide act on the loop of Henle, providing a more potent diuretic effect but may lead to greater electrolyte imbalances. Potassium-sparing diuretics, such as spironolactone, disrupt sodium reabsorption while conserving potassium, making them suitable for patients who need to avoid potassium depletion.
Side Effects and Monitoring
While HCTZ is generally well-tolerated, it can cause electrolyte imbalances, particularly low potassium levels, necessitating regular monitoring. Loop diuretics also carry a higher risk of electrolyte disturbances but are often chosen for more severe edema or heart failure. Potassium-sparing diuretics offer a safe alternative regarding potassium levels but may lead to hyperkalemia if not monitored properly. Each diuretic’s side effects dictate careful patient selection based on individual health needs and conditions.
In therapeutic practice, choosing between these diuretics hinges on the patient’s specific circumstances, including blood pressure levels, existing medical conditions, and potential for side effects. Hydrochlorothiazide remains a foundational treatment for hypertension, providing a balance between efficacy and safety.