Addressing hypothalamic amenorrhea often involves lifestyle modifications and medical treatments. If you’re struggling with this condition, Clomid may offer a path to restore normal menstrual function. This medication stimulates ovarian function, potentially helping to reinitiate your cycle.
Incorporating Clomid into your treatment plan requires careful monitoring and consultation with a healthcare provider. Expect a thorough evaluation of your hormonal levels and overall health before starting. Regular follow-ups ensure the effectiveness of the treatment and allow for necessary adjustments.
While Clomid can be a beneficial tool, pairing it with lifestyle changes, such as nutrition and stress management, enhances your chances of restoring menstrual regularity. Focus on balanced meals and moderate exercise to support your hormonal health.
Establish open communication with your healthcare team, discussing any concerns or side effects you may encounter during the treatment. Staying informed and engaged in your care can lead to better outcomes and a smoother journey toward reproductive health.
- Hypothalamic Amenorrhea and Clomid
- Understanding Hypothalamic Amenorrhea: Causes and Symptoms
- Causes
- Symptoms
- The Role of Clomid in Treating Hypothalamic Amenorrhea
- Mechanism of Action
- Dosage and Administration
- Evaluating the Efficacy of Clomid: Success Rates and Considerations
- Potential Side Effects of Clomid in Patients with Hypothalamic Amenorrhea
- Integrating Lifestyle Changes for Improved Outcomes with Clomid
Hypothalamic Amenorrhea and Clomid
For individuals experiencing hypothalamic amenorrhea, Clomid (clomiphene citrate) offers a potential pathway to restore menstrual cycles and improve fertility. This medication stimulates the release of hormones necessary for ovulation.
Consider the following when using Clomid for hypothalamic amenorrhea:
- Diagnosis Confirmation: Ensure a healthcare provider diagnoses hypothalamic amenorrhea before initiating Clomid. Rule out other underlying conditions.
- Weight Management: Address any issues related to weight, as significant weight loss or gain can affect hormonal balance. Aiming for a healthy weight may improve response to Clomid.
- Dosage and Timing: Clomid is typically taken for five days early in the menstrual cycle. Follow the prescribed dosage carefully for optimal results.
- Monitoring Ovulation: Regular monitoring, such as ultrasound or lab testing, can help track ovulation and assess Clomid’s effectiveness.
- Potential Side Effects: Be aware of possible side effects, including hot flashes, mood swings, and ovarian hyperstimulation. Report any severe reactions to a healthcare provider.
- Alternative Treatments: If Clomid isn’t effective, discuss alternative options with your doctor. Other fertility treatments may be available.
Clomid can be helpful for those dealing with hypothalamic amenorrhea, but it requires careful management and frequent consultation with a healthcare provider to ensure safe and effective treatment.
Understanding Hypothalamic Amenorrhea: Causes and Symptoms
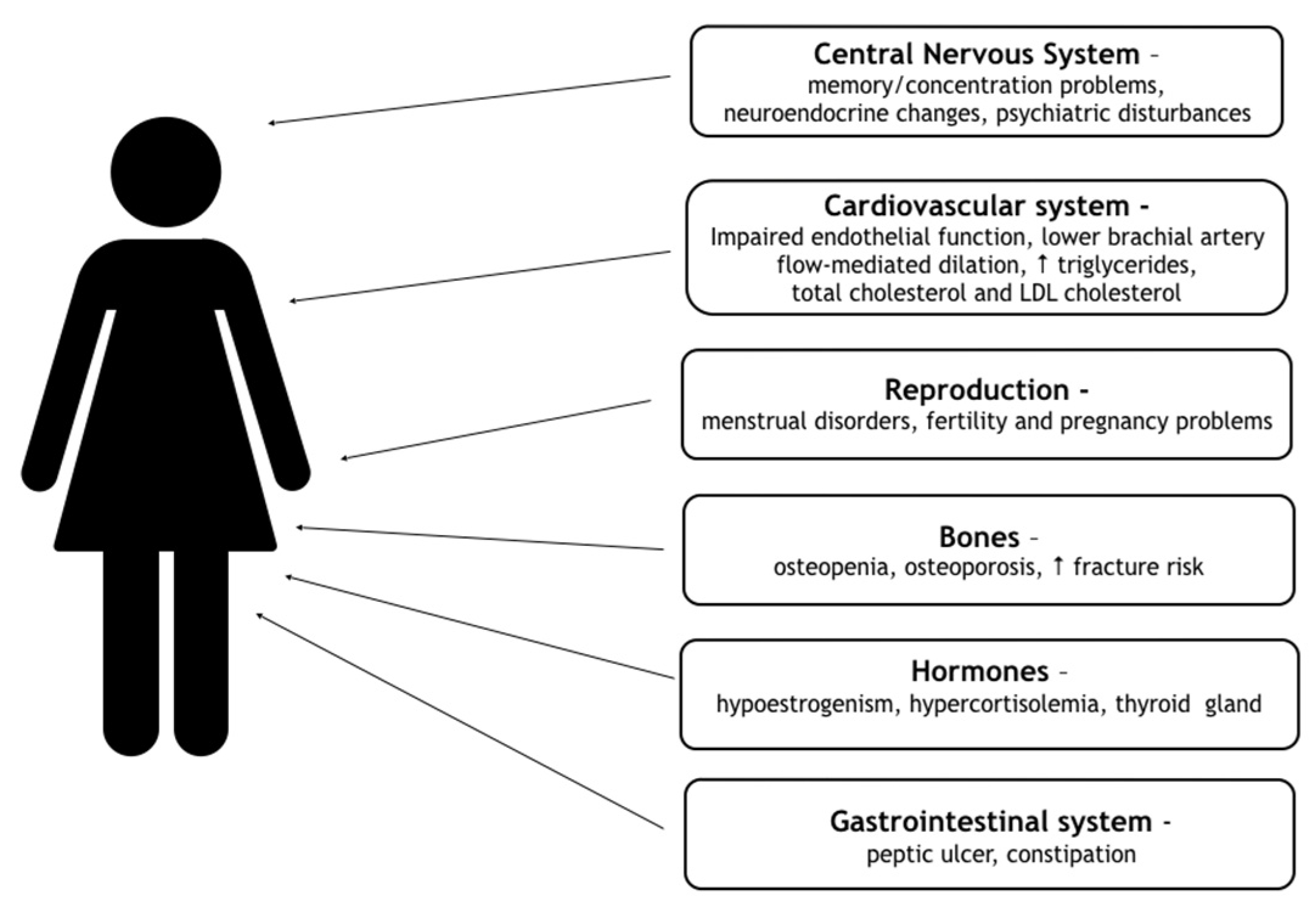
Hypothalamic amenorrhea occurs when the hypothalamus stops producing hormones that trigger menstrual cycles. This disruption causes missed periods and can impact fertility. Identifying the causes is crucial for effective management.
Causes
Stress significantly influences hypothalamic function. High levels of stress from work, personal issues, or other sources can disturb hormone release. Another factor is low body weight, often due to restrictive eating or excessive exercise. Nutritional deficiencies can also play a role, as the body needs sufficient energy and nutrients to maintain reproductive health. Additionally, medical conditions such as polycystic ovary syndrome (PCOS) or thyroid disorders may contribute.
Symptoms
The most evident symptom is the absence of menstrual periods. Women may also experience symptoms like fatigue, insomnia, mood changes, and decreased libido. It’s common to notice changes in appetite or weight fluctuations. Consulting a healthcare professional can aid in diagnosing and addressing these symptoms effectively.
Addressing hypothalamic amenorrhea often involves lifestyle adjustments, including stress management, achieving a healthy weight, and ensuring a balanced diet. Restoration of menstrual cycles can lead to improved overall well-being and fertility outcomes.
The Role of Clomid in Treating Hypothalamic Amenorrhea
Clomid, or clomiphene citrate, serves as a key option for women experiencing hypothalamic amenorrhea. By stimulating the hypothalamus and pituitary gland, Clomid encourages the production of hormones necessary for ovulation. This can restore menstrual cycles in individuals whose periods have been disrupted due to factors like excessive exercise, low body weight, or stress.
Mechanism of Action
Clomid works by blocking estrogen receptors in the hypothalamus, which tricks the body into thinking estrogen levels are low. Consequently, the pituitary gland increases the secretion of follicle-stimulating hormone (FSH) and luteinizing hormone (LH). The rise in these hormones can prompt ovarian function, facilitating ovulation and the subsequent return of menstruation.
Dosage and Administration
The typical Clomid regimen consists of taking the medication for five days, starting on the fifth day of the menstrual cycle. Initial doses often range from 50 mg to 150 mg, depending on individual response. Regular monitoring through ultrasounds and hormone tests allows healthcare providers to adjust doses effectively to achieve the desired outcome.
In conclusion, Clomid plays a significant role in managing hypothalamic amenorrhea by stimulating ovulation and restoring menstrual health for many women. Consulting a healthcare professional is essential to tailor treatment to individual needs.
Evaluating the Efficacy of Clomid: Success Rates and Considerations
Clomid has shown promising success rates in inducing ovulation among women experiencing hypothalamic amenorrhea. In clinical studies, approximately 60-80% of women using Clomid achieve ovulation within the first few cycles of treatment.
The response to Clomid may vary based on individual circumstances. For women with hypothalamic amenorrhea, factors such as body weight, stress levels, and hormonal balance significantly influence outcomes. Maintaining a healthy body mass index (BMI) can enhance the likelihood of ovulation.
Monitoring should occur throughout the treatment process. Regular check-ups with a healthcare provider help assess both hormonal responses and overall wellbeing. Possible side effects include mood swings, hot flashes, and breast tenderness. Discuss any concerns with a provider to adjust treatment as necessary.
| Success Rates | Description |
|---|---|
| 60-80% | Percentage of women achieving ovulation |
| 30-50% | Chance of conception per cycle post-ovulation |
| 10-20% | Likelihood of multiple pregnancies |
Managing lifestyle factors can further enhance outcomes. Engaging in regular physical activity and adopting stress management techniques support hormonal regulation. Nutrition plays a role as well; a balanced diet rich in vitamins and minerals fortifies reproductive health.
In conclusion, Clomid presents a viable option for women with hypothalamic amenorrhea looking to restore their ovulation cycles. Individualized monitoring and lifestyle adjustments are critical components that can improve the success of Clomid therapy.
Potential Side Effects of Clomid in Patients with Hypothalamic Amenorrhea
Patients with hypothalamic amenorrhea considering Clomid should be aware of several potential side effects. Understanding these effects can help manage expectations and improve the overall treatment experience.
- Hot Flashes: Many patients report experiencing hot flashes due to hormonal fluctuations influenced by Clomid.
- Mood Swings: Emotional changes may occur, including mood swings or increased irritability. Monitoring emotional well-being can be beneficial.
- Visual Disturbances: Some individuals may experience blurred vision or visual disturbances. If these symptoms arise, contacting a healthcare provider is essential.
- Abdominal Discomfort: Mild abdominal bloating or discomfort is common. Keeping track of dietary habits may alleviate some discomfort.
- Ovarian Hyperstimulation Syndrome (OHSS): Though rare, OHSS is a serious condition that may arise, especially if dosages are not appropriately managed. Patients should report any signs of OHSS, such as severe abdominal pain or swelling, difficulty breathing, or rapid weight gain.
- Multiple Pregnancies: Clomid increases the likelihood of multiple ovulations, which may lead to twins or higher-order multiples. Discussions with a healthcare professional about the risks of multiple pregnancies are recommended.
Consultation with a healthcare provider prior to starting Clomid can help tailor the treatment approach, minimize side effects, and address any concerns regarding these potential risks. Regular follow-up appointments are important for monitoring response to treatment and managing side effects effectively.
Integrating Lifestyle Changes for Improved Outcomes with Clomid
Incorporate regular exercise into your routine. Aim for at least 150 minutes of moderate cardio each week, combined with strength training. This improves overall health and balances hormones, enhancing Clomid’s effectiveness.
Focus on a balanced diet rich in fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and lean proteins. Include foods high in antioxidants, like berries and leafy greens, to support reproductive health. Omega-3 fatty acids found in fish or flaxseed can also be beneficial.
Practice stress management techniques. Mindfulness, yoga, and meditation can help lower cortisol levels, which negatively impact hormone regulation. Devote time daily to activities that bring you joy and relaxation.
Prioritize sleep quality. Aim for 7-9 hours of restful sleep each night. Create a calming bedtime routine, limit screen time before bed, and maintain a consistent sleep schedule to support hormonal balance.
Stay hydrated. Drinking adequate water helps regulate body functions, including hormone production. Aim for at least 8 cups of water daily, adjusting based on activity level and personal needs.
Avoid smoking and limit alcohol intake. Both can have adverse effects on fertility and hormone levels. Reduce or eliminate these substances for better reproductive health.
Consult with a healthcare provider for personalized recommendations. Regular check-ups can help monitor your progress and make necessary adjustments to your treatment plan.