If you are taking Paxil (paroxetine) and notice changes in your hormonal balance, it’s critical to consult your healthcare provider. Paxil can potentially affect the pituitary gland, leading to various hormonal disruptions. Monitoring your symptoms closely can help in identifying any issues early.
The pituitary gland plays a significant role in hormone regulation, affecting growth, metabolism, and stress response. Paxil may alter the secretion of hormones from this gland, resulting in conditions like prolactinomas or adrenal insufficiency. Regular blood tests can assess hormone levels to ensure they remain within a healthy range.
For those experiencing fatigue, mood swings, or unexpected weight changes while on Paxil, keep a detailed record of your symptoms, including their onset and duration. This information will be invaluable during your discussions with health professionals, enabling tailored adjustments to your treatment plan. Stay proactive in your care to maintain optimal health and well-being.
- Paxil and Pituitary Gland Disorder
- Understanding the Relationship
- Recommendations for Patients
- Understanding Paxil’s Role in Mental Health
- The Anatomy and Function of the Pituitary Gland
- How Paxil Affects Hormonal Regulation by the Pituitary Gland
- Common Pituitary Gland Disorders Linked with Paxil Use
- Hypopituitarism
- Growth Hormone Deficiency
- Symptoms of Pituitary Gland Disorders Associated with Paxil
- Managing Pituitary Gland Disorders While on Paxil
- Consulting Healthcare Professionals about Paxil and Pituitary Health
- Key Topics to Address
- Monitoring Your Health
Paxil and Pituitary Gland Disorder
Paxil, known generically as paroxetine, is an antidepressant that can influence hormonal balance, particularly affecting the pituitary gland. It is crucial to monitor any changes in symptoms related to hormonal alterations when using Paxil. Individuals may experience fluctuations in mood, weight, energy levels, and sexual function, often stemming from the impacts on hormonal regulation.
Understanding the Relationship
The pituitary gland plays a central role in hormonal secretion, including hormones that regulate stress response, growth, and reproduction. Paxil may disrupt these functions, leading to conditions like hyperprolactinemia, which results in elevated prolactin levels. This can cause menstrual irregularities, sexual dysfunction, and changes in libido. Regular screening and communication with healthcare providers about any unusual symptoms can help manage these side effects effectively.
Recommendations for Patients
For individuals prescribed Paxil, adhere to the prescribed dosage and schedule. Report any changes in mood, weight, or sexual health to a healthcare professional promptly. Collaborate with your doctor to evaluate potential alternatives or additional treatments if side effects become concerning. Regular hormonal assessments can also be beneficial in managing and adjusting treatment strategies as needed.
Understanding Paxil’s Role in Mental Health
Paxil, or paroxetine, functions as a selective serotonin reuptake inhibitor (SSRI). This medication enhances serotonin levels in the brain, a key neurotransmitter linked to mood regulation. When prescribed for conditions like depression and anxiety, Paxil can lead to significant improvements in emotional well-being.
Start treatment at a low dose, allowing your healthcare provider to adjust it based on your response. Monitor changes in mood, anxiety levels, and any side effects. Common side effects may include nausea, fatigue, or sexual dysfunction, which require discussion with your doctor if they persist or worsen.
Engaging in therapy alongside Paxil use amplifies its positive effects. Cognitive-behavioral therapy (CBT) particularly complements medication, providing tools to manage symptoms effectively. Incorporating lifestyle modifications like regular exercise, proper nutrition, and adequate sleep enhances overall mental health outcomes.
Understand the importance of consistency when taking Paxil. Skipping doses can lead to withdrawal symptoms or a resurgence in anxiety and depressive episodes. If you decide to stop taking Paxil, consult your doctor for a tapering plan to minimize potential withdrawal effects.
Regular follow-ups with your healthcare provider are key. Adjustments in your treatment regimen may be necessary based on your progress. Staying informed about any changes in your mental health or side effects allows for timely interventions.
Paxil can provide substantial relief for many individuals struggling with mental health disorders. Through careful management and support, you can maximize the benefits of this medication and improve your quality of life.
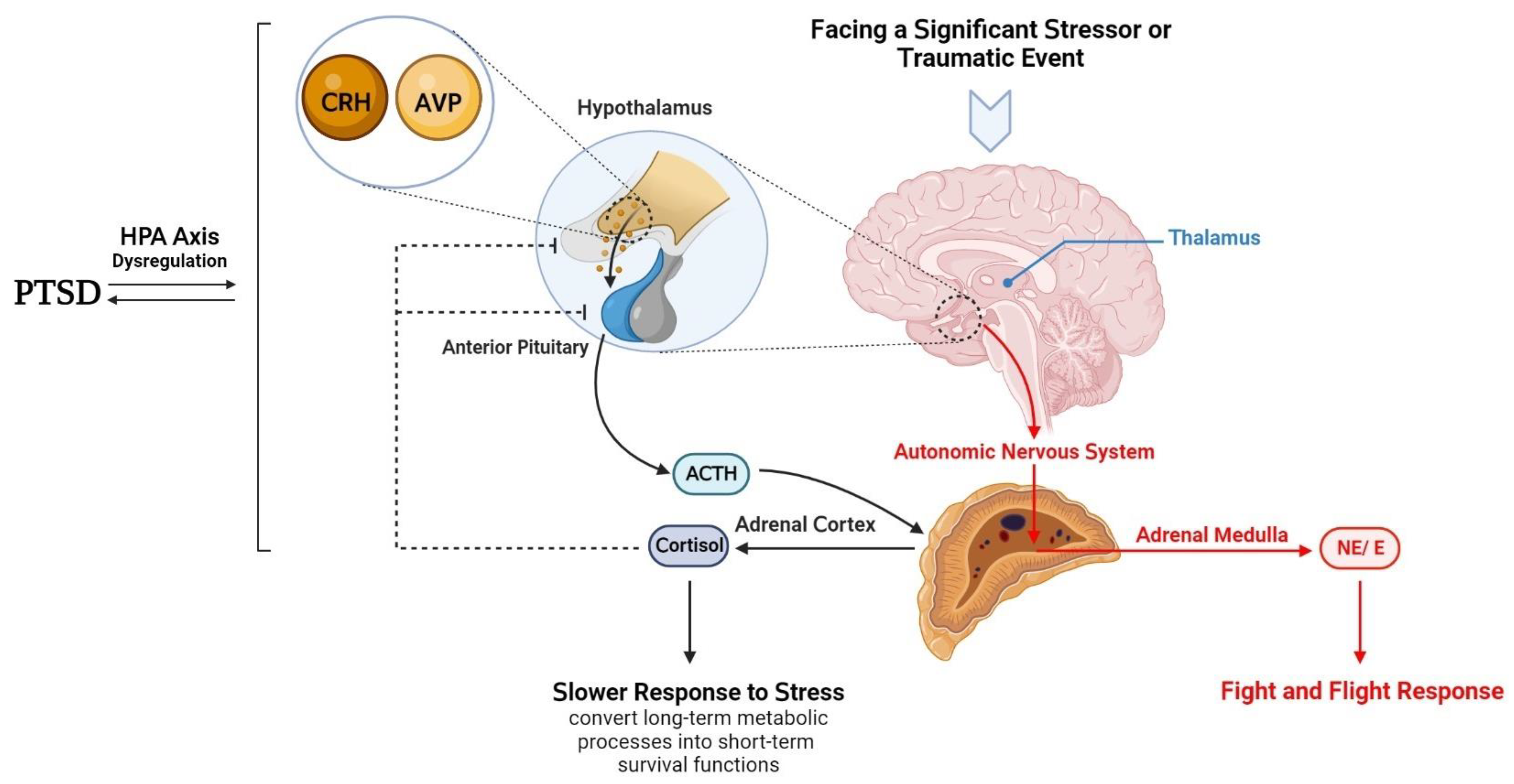
The Anatomy and Function of the Pituitary Gland
The pituitary gland, often dubbed the “master gland,” plays a pivotal role in regulating various bodily functions. This pea-sized structure resides at the base of the brain, beneath the hypothalamus. Its strategic location allows it to efficiently communicate with the brain and the rest of the endocrine system.
The pituitary gland consists of two primary lobes: the anterior pituitary and the posterior pituitary. Each lobe has distinct functions and hormone production capabilities.
- Anterior Pituitary: This lobe produces hormones that influence growth, metabolism, and reproduction. Key hormones include:
- Growth Hormone (GH): Stimulates growth and cell reproduction.
- Prolactin (PRL): Regulates milk production in breastfeeding women.
- Adrenocorticotropic Hormone (ACTH): Stimulates cortisol production from the adrenal glands.
- Thyroid-Stimulating Hormone (TSH): Promotes thyroid hormone release, impacting metabolism.
- Luteinizing Hormone (LH) and Follicle-Stimulating Hormone (FSH): Control reproductive processes in both sexes.
- Posterior Pituitary: This lobe stores and releases hormones produced in the hypothalamus. It primarily releases:
- Oxytocin: Facilitates childbirth and lactation, enhancing maternal bonding.
- Vasopressin (Antidiuretic Hormone, ADH): Regulates water balance by controlling kidney function.
Designed to maintain homeostasis, the pituitary gland interacts with various organs. It sends hormonal signals that affect the adrenal glands, thyroid gland, and reproductive organs. This intricate feedback loop helps maintain balance in numerous bodily functions, including stress response, growth, and metabolism.
Understanding the structure and functions of the pituitary gland is crucial for recognizing its impact on overall health. Regular monitoring of hormonal balance can help detect potential disorders linked to this gland, highlighting the importance of seeking medical advice if symptoms arise.
How Paxil Affects Hormonal Regulation by the Pituitary Gland
Paxil can influence the hormonal regulation handled by the pituitary gland, specifically by altering serotonin levels. This change can affect the release of hormones such as ACTH (adrenocorticotropic hormone), which subsequently impacts cortisol production in the adrenal glands. Elevated cortisol levels can lead to various metabolic changes and potentially increase stress responses.
This medication also interacts with the hypothalamic-pituitary-gonadal axis, which is crucial for reproductive hormone regulation. Some users may experience changes in libido or menstrual irregularities due to these hormonal shifts, particularly in women.
Moreover, studies indicate that Paxil can affect growth hormone release. Persistent use may lead to alterations in growth hormone secretion patterns, impacting overall metabolism and energy regulation.
For any individual considering Paxil, monitoring hormonal levels through regular check-ups is advisable. Collaborating with healthcare providers ensures that any hormonal imbalances are promptly addressed. Making informed decisions about treatment options can significantly enhance the management of symptoms while minimizing side effects.
Common Pituitary Gland Disorders Linked with Paxil Use
Paxil, a selective serotonin reuptake inhibitor (SSRI), has been associated with various pituitary gland disorders. One common issue is hyperprolactinemia, characterized by elevated prolactin levels. This condition may lead to symptoms such as irregular menstrual cycles in women and decreased libido or erectile dysfunction in men. Monitoring prolactin levels during treatment with Paxil is advisable for those experiencing unexpected hormonal changes.
Hypopituitarism
Another disorder linked with Paxil use is hypopituitarism, a condition where the pituitary gland fails to produce adequate amounts of one or more of its hormones. Symptoms can include fatigue, weight gain, and decreased stress tolerance. If you start to notice significant changes in energy levels or mood stability, consult with a healthcare provider to evaluate pituitary functioning.
Growth Hormone Deficiency
Growth hormone deficiency can also arise when using Paxil. Individuals may experience reduced muscle mass, increased fat accumulation, and decreased bone density. Regular assessment of growth hormone levels can help identify this deficiency early, allowing for timely intervention.
Symptoms of Pituitary Gland Disorders Associated with Paxil
Pituitary gland disorders related to Paxil may manifest through various symptoms. Users should watch for notable changes in mood and energy levels. Depression or anxiety symptoms may intensify, leading to emotional instability.
Weight fluctuations often occur, resulting in either significant weight loss or gain. This shift can be linked to hormonal imbalances caused by the pituitary gland’s dysfunction. Additionally, disruptions in sleep patterns, including insomnia or excessive sleepiness, should not be overlooked.
Reproductive health may also be affected. Individuals may experience altered menstrual cycles or symptoms of sexual dysfunction. Fertility issues can arise due to hormonal changes impacting reproductive hormones.
Physical symptoms include unexplained headaches or visual disturbances, particularly if the pituitary disorder leads to increased pressure in the skull. These issues demand prompt medical attention.
Monitoring other potential symptoms like fatigue, low libido, or persistent thirst and urination is also crucial. Each symptom reflects the delicate balance maintained by the pituitary gland.
If experiencing these symptoms while taking Paxil, consult a healthcare provider to evaluate potential links and discuss appropriate management strategies.
Managing Pituitary Gland Disorders While on Paxil
Consult with your healthcare provider to regularly monitor your pituitary function while taking Paxil. Schedule blood tests to check hormone levels and adjust your treatment plan as necessary.
Adhere to a balanced diet rich in vitamins and minerals to support hormonal health. Focus on foods high in omega-3 fatty acids, antioxidants, and whole grains. Consider including:
- Fish such as salmon and mackerel
- Fruits and vegetables like berries and leafy greens
- Nuts and seeds for healthy fats
Incorporate regular physical activity into your routine, as exercise can aid in maintaining hormonal balance. Aim for at least 30 minutes of moderate exercise most days. Options include:
- Walking or jogging
- Yoga for stress management
- Cycling or swimming
Manage stress effectively, since it can exacerbate pituitary disorders. Techniques such as mindfulness meditation, deep breathing exercises, and progressive muscle relaxation can be beneficial.
Keep track of any new symptoms that arise during treatment. Changes in mood, energy levels, or weight can indicate shifts in hormone production. Document these changes to discuss with your doctor.
Maintain open communication with your healthcare team. Sharing your experiences and concerns helps in tailoring your treatment approach and ensures you receive the support needed to manage your condition.
Consider consulting an endocrinologist for specialized advice on pituitary disorders. They can provide further insights and strategies specific to your situation.
Consulting Healthcare Professionals about Paxil and Pituitary Health
Engage with your healthcare professional before starting or continuing Paxil if you have concerns about pituitary health. Discuss any symptoms you experience, such as changes in mood, weight fluctuations, or hormonal irregularities, as these can be indicators of pituitary gland issues. Accurate communication ensures appropriate management of your condition.
Key Topics to Address
Focus on the following areas during your consultation:
- Current medications and their interactions.
- Personal and family medical history related to mood disorders and pituitary disturbances.
- Any hormonal symptoms such as fatigue or metabolism changes.
- Planned evaluations, including blood tests or imaging, if needed.
Monitoring Your Health
Regular follow-ups are essential for assessing the effectiveness of Paxil in managing symptoms while monitoring for potential side effects. Your healthcare provider may adjust your dosage or explore alternative treatments based on your progress and overall health status.
| Symptom | Action |
|---|---|
| Mood changes | Report to your healthcare professional |
| Unexplained weight gain/loss | Schedule a check-up |
| Fatigue | Discuss potential hormonal assessments |
| Changes in menstrual cycle | Consult with a specialist if needed |
Being proactive in your healthcare discussions ensures better outcomes. Adhering to medical advice and regularly monitoring your health will help you manage both your mental well-being and any potential pituitary health concerns effectively.