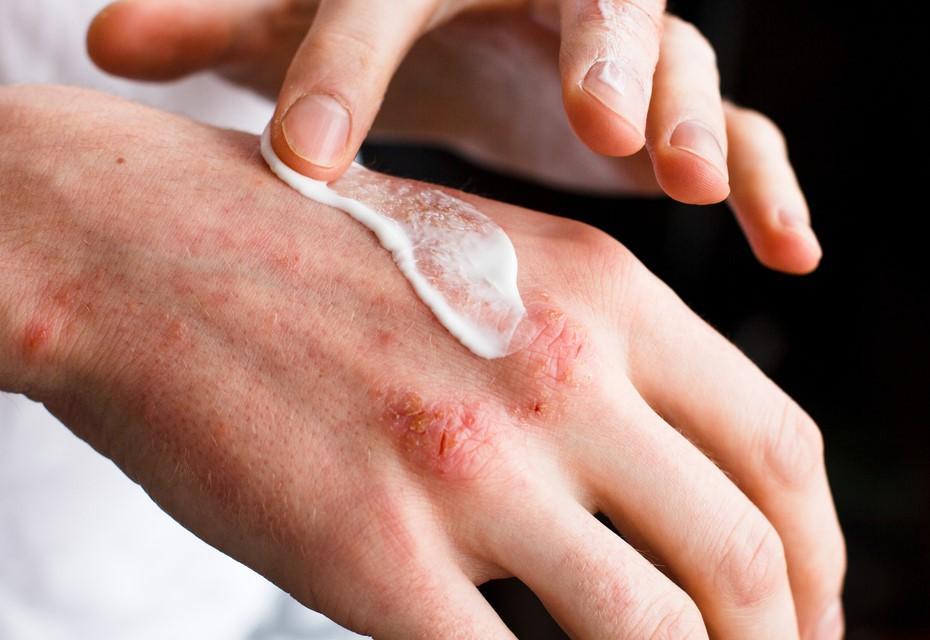
For individuals struggling with skin disorders, prednisone frequently offers a reliable solution to reduce inflammation and alleviate symptoms. This corticosteroid serves as a powerful anti-inflammatory agent, making it ideal for conditions like eczema, psoriasis, and dermatitis. By modulating the immune response, prednisone effectively curbs the overactive reactions that lead to redness, swelling, and discomfort.
When prescribed by a healthcare professional, prednisone can improve the quality of life for those experiencing persistent skin issues. Dosing typically starts at lower levels, allowing for adjustments based on the patient’s response and any observed side effects. Monitoring is crucial, as long-term use may lead to complications that warrant a careful approach to tapering the dosage.
In addition to its immediate effects, prednisone can enhance the results of topical treatments. Pairing oral medication with creams or ointments can maximize relief and promote faster healing. Always heed medical advice regarding the duration of treatment to minimize potential side effects and optimize skin health.
- Prednisone for Treatment of Skin Disorders
- Understanding Prednisone and Its Mechanism of Action
- Mechanism of Action
- Clinical Use in Skin Disorders
- Common Skin Disorders Treated with Prednisone
- Psoriasis
- Dermatitis
- Dosage Guidelines for Skin Disorders
- Potential Side Effects of Prednisone for Skin Conditions
- Indications for Long-Term vs. Short-Term Use
- Alternatives to Prednisone for Skin Disorders
- Patient Experiences and Case Studies
- Personal Insights and Long-term Management
- Conclusion of Reflections
- Consultation and Management for Prednisone Therapy
Prednisone for Treatment of Skin Disorders
Prednisone is often prescribed for a range of skin disorders due to its potent anti-inflammatory properties. Conditions such as eczema, psoriasis, and dermatitis respond well to this corticosteroid. Patients typically see improvements in redness, swelling, and itching within a short period.
The dosage of prednisone varies depending on the severity of the disorder. Starting with a higher dose can provide quicker relief, followed by a gradual tapering to minimize potential side effects. It’s crucial to follow your healthcare provider’s instructions regarding dosage and duration.
Monitoring for side effects is essential. While prednisone effectively reduces inflammation, it can cause issues like weight gain, mood swings, and increased blood pressure. Regular consultations with a healthcare professional help manage these risks effectively.
Combining prednisone with topical treatments can enhance overall effectiveness. For instance, using potent topical corticosteroids alongside systemic prednisone can target inflammation on the skin’s surface while managing deeper symptoms.
For long-term management of chronic conditions, consider lifestyle adjustments alongside prednisone therapy. Maintaining a healthy diet, managing stress, and following a skincare routine tailored to your specific disorder can contribute to better outcomes.
Consultation with a dermatologist may provide additional strategies and treatment options, particularly for persistent or severe cases. Understanding your specific skin condition allows for a more personalized approach to therapy.
Understanding Prednisone and Its Mechanism of Action
Prednisone acts as a powerful anti-inflammatory medication, commonly used to treat various skin disorders. It mimics the effects of cortisol, a hormone naturally produced by the adrenal glands. By modulating the immune response, prednisone minimizes inflammation and suppresses overactive immune reactions.
Mechanism of Action
The mechanism of action involves several key processes:
- Glucocorticoid Receptor Activation: Prednisone binds to glucocorticoid receptors present in the cytoplasm of cells. This activation triggers a cascade of anti-inflammatory responses.
- Inhibition of Pro-Inflammatory Cytokines: The drug decreases the production of pro-inflammatory cytokines and mediators, leading to reduced swelling, redness, and pain.
- Reduction of Immune Cell Activity: Prednisone dampens the activity of immune cells such as lymphocytes and macrophages, which contribute to inflammation.
- Enhancement of Lipocortin Production: This leads to inhibition of phospholipase A2, an enzyme involved in the production of inflammatory mediators like prostaglandins and leukotrienes.
Clinical Use in Skin Disorders
Healthcare providers prescribe prednisone for conditions such as eczema, psoriasis, and severe allergic reactions. Typical dosing varies based on the severity of the disorder and patient response. It’s crucial to monitor for side effects, including increased susceptibility to infections and potential changes in mood or sleep patterns.
Ongoing assessment and adjustment of the treatment plan ensure optimal results while minimizing risks. Always consult a healthcare professional before starting or altering prednisone therapy.
Common Skin Disorders Treated with Prednisone
Prednisone is frequently used to address various inflammatory skin disorders. This corticosteroid works by reducing inflammation and suppressing the immune response, providing significant relief for several conditions.
Psoriasis
Prednisone serves as an effective treatment for psoriasis, particularly during flare-ups. It reduces redness and scaling, improving skin appearance and comfort. Short-term courses can provide rapid relief, although long-term use should be carefully monitored due to potential side effects.
Dermatitis
Contact dermatitis and atopic dermatitis often respond well to prednisone therapy. In cases of severe itching and inflammation, prednisone can quickly alleviate symptoms. Patients typically notice a decrease in swelling and irritation within days, leading to a more comfortable experience.
For both psoriasis and dermatitis, a healthcare provider will determine the appropriate dosage and duration based on individual response and condition severity. Regular follow-ups ensure optimal treatment outcomes.
Dosage Guidelines for Skin Disorders
The typical starting dose of prednisone for skin disorders ranges from 10 to 40 mg per day, depending on the severity of the condition and individual response. For many, a dose of 20 mg daily often provides beneficial results.
For acute inflammatory skin conditions, such as eczema or dermatitis, consider initiating treatment with 20 to 40 mg daily. Assess the patient’s response after one week, then adjust the dosage accordingly, typically reducing to a maintenance level of 5 to 15 mg daily if improvement is observed.
In chronic conditions, like psoriasis, a lower long-term dosage of 5 to 15 mg daily may suffice after achieving control with a higher initial dose. Monitor patients closely for any side effects or signs of rebound flare-ups as the dosage decreases.
For cases with severe symptoms, a higher initial dose of up to 60 mg daily may be necessary. Taper the dosage gradually over 1-2 weeks to minimize withdrawal symptoms and prevent flares.
Always consider the patient’s individual health status, weight, and coexisting conditions when determining dosage. Regular follow-ups help to evaluate effectiveness and make necessary adjustments.
Use caution when prescribing prednisone for extended periods. Aim to limit the duration to avoid potential side effects while ensuring treatment remains beneficial.
Potential Side Effects of Prednisone for Skin Conditions
Beware of the potential side effects when using prednisone for skin conditions. While it can effectively reduce inflammation and alleviate symptoms, some adverse reactions may arise.
- Weight Gain: Fluid retention and increased appetite can lead to noticeable weight gain during treatment.
- Skin Changes: Users may experience thinning skin, easy bruising, or delayed wound healing.
- Gastrointestinal Issues: Nausea, increased risk of ulcers, or heartburn can occur, especially with longer use.
- Mood Swings: Some report feeling anxious, irritable, or experiencing mood changes.
- Insomnia: Difficulty sleeping can be a common complaint, affecting overall well-being.
- Increased Blood Sugar: Monitoring may be needed for those with diabetes or at risk.
- Immune Suppression: Consider higher susceptibility to infections due to immune system weakening.
Regular monitoring by a healthcare provider helps manage these side effects. Discuss any signs or symptoms that arise during treatment to adjust the dosage or explore alternatives if necessary.
Stay proactive in addressing side effects to minimize discomfort while treating skin conditions effectively.
Indications for Long-Term vs. Short-Term Use
Short-term use of prednisone is typically recommended for acute inflammatory skin conditions such as contact dermatitis, severe eczema, or psoriasis flare-ups. Treatment duration often spans from a few days to a couple of weeks, helping to quickly reduce inflammation and provide relief. Dosage usually starts high and tapers down to minimize potential side effects. This approach effectively manages symptoms without excessive risk.
Long-term use, however, may be indicated for chronic skin disorders like severe autoimmune conditions, including lupus or dermatomyositis. In such cases, prednisone serves to control ongoing inflammation and prevent exacerbations. The healthcare provider must carefully monitor dosage and side effects, often aiming to use the minimal effective dose. Patients should undergo regular evaluations to assess treatment necessity and adjust based on their response.
For patients transitioning from short to long-term use, maintaining communication with healthcare providers is crucial. Adjustments may be required based on side effects or the development of tolerance. Monitoring for complications such as hypertension or osteoporosis becomes increasingly important with prolonged treatment.
In conclusion, the decision between long-term and short-term prednisone use hinges on the specific skin disorder, severity, and individual patient response. Close supervision ensures benefits outweigh risks, allowing for an optimal treatment strategy.
Alternatives to Prednisone for Skin Disorders
Consider topical corticosteroids for localized inflammation and irritation. These medications come in various strengths, allowing tailored treatment for conditions like eczema and psoriasis while minimizing systemic side effects.
Calcineurin inhibitors, such as tacrolimus or pimecrolimus, offer a non-steroidal option. They effectively reduce inflammation and can be beneficial for sensitive skin areas, providing relief without the risks associated with long-term steroid use.
For inflammatory skin conditions, phototherapy presents another approach. Exposure to controlled amounts of ultraviolet light can significantly improve symptoms of conditions like psoriasis and eczema. Consult a dermatologist for a suitable plan.
Antihistamines may alleviate itching and discomfort related to allergic reactions. Both over-the-counter and prescription options can help manage symptoms, enabling better skin comfort.
Natural remedies such as aloe vera, chamomile, or calendula can soothe irritated skin. While evidence varies, many find these options helpful for mild skin disorders, promoting healing and relief.
Dietary adjustments can also support skin health. Incorporating anti-inflammatory foods, like omega-3 fatty acids from fish, may enhance skin condition over time. Staying hydrated and avoiding known allergens contributes positively as well.
Finally, explore biologics for chronic conditions unresponsive to other therapies. These advanced medications target specific components of the immune system, offering relief for severe psoriasis and eczema.
Patient Experiences and Case Studies
Many patients report significant improvements in their skin disorders after starting prednisone. One individual with severe eczema found that within a week of treatment, their skin condition improved dramatically, allowing them to resume normal activities without discomfort. This quick response often motivates healthcare providers to consider prednisone as an immediate option for managing severe flares.
A case study involving a patient with psoriasis demonstrated the importance of dosage adjustment. Initially prescribed a high dose, the patient experienced rapid improvement but also some side effects, such as weight gain and mood swings. After consulting their doctor, the dosage was decreased, leading to a balanced approach that managed the skin condition while minimizing adverse effects.
Personal Insights and Long-term Management
Another patient shared their experience with prednisone in combination with topical treatments. They noted that while prednisone was effective in controlling inflammation, maintaining results required ongoing care with dermatological products. This combination allowed the patient to transition off prednisone over time, avoiding long-term use while still managing their skin disorder effectively.
Patients also shared their concerns about potential side effects. One user reported insomnia and increased appetite but affirmed that these were manageable and outweighed by the benefits of resolving their skin issues. Regular follow-up appointments helped keep these side effects under control and allowed adjustments to the treatment plan as necessary.
Conclusion of Reflections
Patient testimonials emphasize the necessity of clear communication with healthcare providers regarding experiences on prednisone. Many felt that understanding the medication’s effects, potential side effects, and management strategies helped them feel more empowered in their treatment journeys. These shared experiences underline the collaborative effort needed to optimize the use of prednisone for skin disorders.
Consultation and Management for Prednisone Therapy
Consult with a healthcare provider before initiating prednisone therapy for skin disorders. This step ensures an accurate diagnosis and appropriate dosage tailored to individual needs. Discuss your medical history, current medications, and any allergies to avoid adverse reactions. A thorough evaluation allows the provider to weigh the benefits against potential risks.
Monitor for side effects throughout treatment. Common concerns include weight gain, mood changes, and increased blood pressure. Regular follow-ups will help assess not only symptom improvement but also monitor these side effects closely.
Dosage adjustments may be necessary. Start with a higher dose for quicker results, then taper gradually to determine the lowest effective dose. This method minimizes side effects while maintaining therapeutic benefits. Maintain clear communication with your healthcare provider during this process.
Consider potential drug interactions. Inform the healthcare provider about all medications, including over-the-counter drugs and supplements. This information prevents complications and enhances treatment safety.
Establish a management plan that includes lifestyle modifications. Balanced nutrition and regular physical activity support overall health and mitigate some side effects of prednisone, such as weight gain and mood swings. Encourage patients to maintain a healthy sleep schedule for better recovery.
| Potential Side Effects | Management Strategies |
|---|---|
| Weight gain | Monitor diet and exercise regularly. |
| Mood changes | Engage in stress-relief activities like yoga or meditation. |
| Increased blood pressure | Regularly check blood pressure; adjust diet to reduce sodium. |
| Increased risk of infection | Avoid close contact with sick individuals; practice good hygiene. |
Educate patients about recognizing signs of serious side effects. Immediate medical attention may be required for symptoms like severe headache, vision changes, or signs of infection. Empowering patients to identify these signs enhances safety and promotes proactive management.
Finally, encourage adherence to prescribed therapy. Skipping doses or abrupt discontinuation can lead to withdrawal symptoms or flares of the underlying disorder. Foster open conversations with healthcare providers to address any concerns about therapy. This collaboration enhances the effectiveness of treatment.