Limit long-term prednisone use to the lowest effective dose for the shortest duration necessary. Chronic use can lead to significant side effects, including osteoporosis, weight gain, and increased risk of infections. Regular monitoring by a healthcare professional is essential to adjust therapy and mitigate risks.
Consider supplemental medications to counteract potential side effects. For instance, calcium and vitamin D can support bone health, while lifestyle modifications such as regular exercise and a balanced diet can manage weight gain. Stay informed about signs of complications, such as persistent fatigue or unusual bruising, to address issues early.
Communicate openly with your healthcare provider regarding any challenges you face while on prednisone. Discussing your symptoms, concerns, or any changes you experience can lead to timely adjustments in your treatment plan. Monitoring blood sugar levels is particularly important for those with a history of diabetes, as prednisone can elevate glucose levels.
In summary, while prednisone can be highly effective for managing various conditions, responsible use and proactive management of side effects can significantly enhance quality of life. Always prioritize your health by staying informed and engaged in your treatment process.
- Prednisone Long Term Use
- Understanding Prednisone: What It Is and How It Works
- How Prednisone Functions
- Long-Term Use Considerations
- Common Conditions Treated with Long-Term Prednisone
- Potential Side Effects of Long-Term Prednisone Use
- Other Side Effects
- Long-Term Management
- Monitoring and Managing Risks During Long-Term Use
- Alternative Treatments to Consider Alongside Prednisone
- Dietary Adjustments
- Stress Reduction Techniques
- Guidelines for Dosage and Tapering Off Prednisone
- Patient Support and Resources for Long-Term Prednisone Users
- Medication Adherence and Management
- Nutritional Guidance
Prednisone Long Term Use
Monitor body weight and blood pressure regularly to prevent complications such as obesity and hypertension. Adjust your diet to include low-sodium and high-potassium foods, which can help counteract some side effects.
Discuss with your healthcare provider about taking calcium and vitamin D supplements to support bone health. Long-term prednisone use can lead to osteoporosis, so focusing on bone strength is key.
Be proactive in managing blood sugar levels. Prednisone can increase blood sugar, posing a risk for diabetes. Regular monitoring and maintaining a balanced diet will contribute to better control.
Incorporate gentle exercises like walking or swimming into your routine to combat potential fatigue and improve overall wellbeing. Engaging in physical activity enhances both mental and physical health.
Stay vigilant about mood changes or psychological effects. Prednisone may influence mood swings or anxiety levels. Keep an open line of communication with your healthcare team for support and adjustments to treatment if necessary.
Regular check-ups are essential. These appointments can help detect any side effects early. Collaborating with your healthcare provider will optimize the benefits of prednisone while managing risks.
Consider establishing a schedule for medication intake. Taking prednisone with food can help minimize gastrointestinal discomfort. Stick to a consistent time each day for improved adherence.
Make use of a patient support group if available. Sharing experiences with others taking prednisone can provide encouragement and practical strategies for managing long-term use.
Explore alternatives and adjunct therapies. Depending on your condition, your provider may suggest other medications or lifestyle adjustments to reduce reliance on prednisone.
Understanding Prednisone: What It Is and How It Works
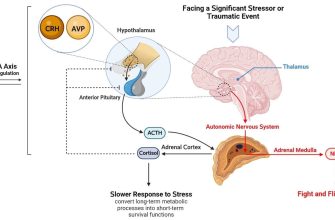
Prednisone is a synthetic corticosteroid commonly prescribed to reduce inflammation and suppress the immune response. It mimics the effects of hormones produced by the adrenal glands. Medical professionals often recommend it for conditions like asthma, arthritis, lupus, and certain allergic reactions.
How Prednisone Functions
This medication works by inhibiting substances in the body that trigger inflammation. It affects the immune system by blocking the release of compounds that cause allergic and inflammatory responses. As a result, patients may experience relief from symptoms associated with chronic illnesses. Dosage and duration vary based on individual needs and the specific condition being treated.
Long-Term Use Considerations
Long-term use of prednisone requires careful monitoring due to potential side effects. These include weight gain, osteoporosis, increased blood sugar levels, and susceptibility to infections. Regular consultations with a healthcare provider ensure appropriate management and adjustments to therapy as needed. Discussing a tapering schedule can also help minimize withdrawal symptoms and adverse reactions when discontinuing the medication.
Common Conditions Treated with Long-Term Prednisone
Long-term prednisone use effectively manages several medical conditions. The following table highlights common ailments treated with this medication:
| Condition | Description | Typical Dosage |
|---|---|---|
| Rheumatoid Arthritis | This autoimmune disorder causes chronic inflammation in joints. | 5-10 mg daily, adjusted based on response. |
| Asthma | Prednisone reduces airway inflammation, improving breathing. | 5-40 mg daily during flare-ups. |
| Lupus | This systemic disease affects various organs; prednisone helps manage symptoms. | 10-60 mg daily, based on disease severity. |
| Multiple Sclerosis (MS) | Used during exacerbations to decrease nerve inflammation. | 200-1000 mg for short courses, typically given intravenously. |
| Inflammatory Bowel Disease (IBD) | Conditions like Crohn’s disease and ulcerative colitis see symptom relief. | 20-60 mg daily, tapering as symptoms improve. |
| Allergic Reactions | Severe allergies and anaphylactic reactions respond well to corticosteroids. | 20-60 mg as a starting dose. |
Regular monitoring is essential while on long-term prednisone. Adjustments to dosage ensure optimal outcomes and minimize side effects. Always consult with a healthcare provider before making changes to your treatment plan.
Potential Side Effects of Long-Term Prednisone Use
Long-term prednisone use can lead to various side effects that require attention. Weight gain is common, driven by increased appetite and altered metabolism. Monitoring food intake and engaging in regular exercise helps manage this issue.
Bone health can deteriorate with consistent prednisone use, resulting in osteoporosis. Consider calcium and vitamin D supplementation, along with weight-bearing exercises, to maintain bone density. Regular bone density scans provide valuable insights into your bone health.
Other Side Effects
Increased risk of infection arises due to prednisone’s immunosuppressive properties. Stay vigilant about hygiene and promptly address any signs of infection. Regular check-ups can assist in early detection of any complications.
Changes in mood and behavior, such as anxiety or irritability, may occur. Communicate with a healthcare provider about these psychological effects; they may consider adjusting the dosage or introducing supportive therapies. Cushing’s syndrome, characterized by features like a rounded face and easy bruising, can also develop from prolonged use. Regular assessments help identify these changes early.
Long-Term Management
Discussing tapering strategies with your doctor is crucial for safely reducing the dose when possible. Collaborating with healthcare professionals ensures a comprehensive approach to managing side effects and maintaining overall well-being while on prednisone.
Monitoring and Managing Risks During Long-Term Use
Regular check-ups with your healthcare provider are critical. Schedule appointments every three to six months to monitor potential side effects associated with long-term prednisone use. Blood tests can help track glucose levels, electrolyte balance, and signs of infection.
Maintain a balanced diet to mitigate weight gain and muscle loss. Focus on:
- Fresh vegetables and fruits
- Lean proteins
- Whole grains
Incorporate regular physical activity. Aim for at least 150 minutes of moderate exercise each week. This can include walking, swimming, or cycling, which improve muscle strength and support bone health.
Bone density should be assessed, especially if prednisone use exceeds three months. Use supplementation with calcium and vitamin D after consulting your doctor. This helps prevent osteoporosis and fractures.
Monitor blood pressure and manage stress levels. Medications or lifestyle changes may be necessary to control hypertension, which can be exacerbated by prednisone.
Watch for symptoms of mood changes or other psychological effects. Open communication with your healthcare team is vital for adjusting treatment as needed.
Stay informed about possible drug interactions. Provide your doctor with a complete list of all medications, supplements, and herbal products you are taking. This can help avoid complications.
Finally, develop a plan for tapering off prednisone under medical supervision when possible. Abrupt discontinuation can lead to withdrawal symptoms and adrenal insufficiency. Maintaining a dialogue with your healthcare provider is key to managing risks effectively.
Alternative Treatments to Consider Alongside Prednisone
Integrating alternative treatments can enhance your overall well-being while using prednisone. Focus on dietary changes, stress management, and supplements to support your health.
Dietary Adjustments
Opt for an anti-inflammatory diet rich in fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and healthy fats. Incorporate foods high in omega-3 fatty acids, like fatty fish and flaxseeds, to help reduce inflammation. Limit processed foods, refined sugars, and trans fats to avoid exacerbating any side effects of prednisone.
Stress Reduction Techniques
Practicing mindfulness and relaxation techniques can significantly lessen stress, which may enhance your treatment results. Consider yoga or meditation, both of which promote relaxation and can improve your mental health. Regular physical activity also plays a role; aim for at least 30 minutes of moderate exercise most days of the week to boost mood and support overall health.
Consult your healthcare provider before making any changes to your treatment plan. These alternatives can provide additional support while managing your condition effectively with prednisone.
Guidelines for Dosage and Tapering Off Prednisone
Begin with the lowest effective dose to manage your condition. This dosage often ranges from 5 mg to 60 mg per day, depending on the individual case.
Assess your response to treatment regularly. If you experience significant improvement, discuss with your healthcare provider the possibility of reducing your dose.
When tapering off prednisone, follow a gradual reduction schedule. Sudden discontinuation can lead to withdrawal symptoms and exacerbation of the underlying condition.
- Decrease the dosage by 5 to 10 mg every 3 to 7 days.
- Monitor for symptoms of adrenal insufficiency, such as fatigue, weakness, and dizziness.
- If symptoms occur, consult your doctor for potential adjustments in the tapering schedule.
Consider tapering over several weeks or months, especially if you’ve been on a high dose or long-term therapy. Individual responses may vary, and your healthcare provider will tailor the plan to your needs.
- Utilize a written plan to track your dosage and any symptoms.
- Communicate any concerns or side effects to your healthcare provider.
- Maintain regular follow-up appointments to evaluate your progress.
Stay hydrated and maintain a balanced diet during the tapering process to support your overall health. Always consult your healthcare provider before making any changes to your medication regimen.
Patient Support and Resources for Long-Term Prednisone Users
Connect with patient support groups. Engaging with others who share similar experiences can provide emotional relief and practical advice. Organizations such as the National Institutes of Health (NIH) offer online forums where users can ask questions and share tips.
Medication Adherence and Management
Track your medication schedule. Utilize apps or simple calendars to monitor dosages and refill times. Consistent adherence helps manage symptoms and reduces the risks of side effects. Discuss any side effects openly with your healthcare provider to adjust your treatment plan if necessary.
Nutritional Guidance
Focus on nutrition. A well-balanced diet can mitigate some side effects of prednisone. Incorporate foods rich in calcium and vitamin D to support bone health, and maintain a high-protein diet to help preserve muscle mass. Consulting a registered dietitian can provide tailored advice based on individual health needs.
Stay informed about potential interactions with other medications. Use resources like MedlinePlus or speak with your pharmacist to ensure safe combinations of treatments.
Regular exercise contributes to overall well-being. Engage in low-impact activities such as walking or swimming to improve physical condition without excessive strain. Check with a physical therapist for personalized exercise regimens that consider your current health status.
Access mental health resources. Therapy can help manage anxiety or depression that may arise from long-term medication use. Online therapy platforms offer flexible options for consultations, making mental health more accessible.
Establish solid communication with your healthcare provider. Schedule regular check-ups to monitor health changes and discuss concerns. Creating an open dialogue ensures that you stay on top of your treatment plan.