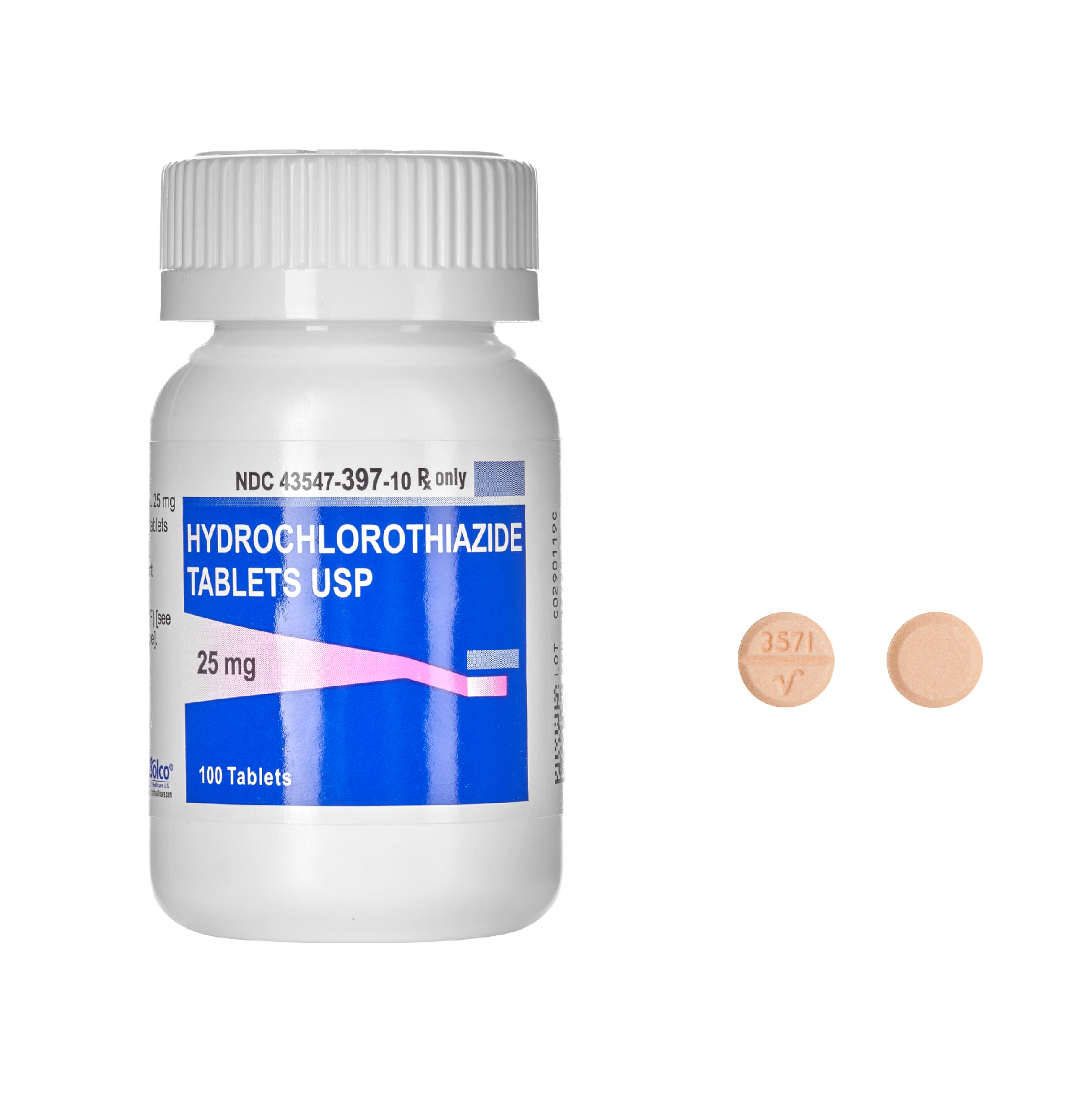
Hydrochlorothiazide is a widely prescribed medication for managing hypertension and reducing fluid retention in patients with heart failure or edema. If your healthcare provider recommends this medication, it’s crucial to understand its uses, dosage, and potential side effects.
This thiazide diuretic functions by promoting the excretion of sodium and water, leading to lower blood pressure. Typically, patients start with a low dose, which may be gradually adjusted based on their response and specific health conditions. Consistent monitoring of blood pressure is advisable to ensure optimal results while minimizing risks.
While hydrochlorothiazide is generally well-tolerated, some individuals may experience side effects such as dizziness, electrolyte imbalances, or increased urination. Regular blood tests can help monitor electrolytes, ensuring that any imbalances are promptly addressed. Always consult your healthcare provider if you notice any unusual symptoms or have concerns regarding your treatment.
Combining hydrochlorothiazide with a healthy lifestyle, including a balanced diet and regular exercise, can enhance its effectiveness in managing your health. Staying hydrated and adhering to prescribed doses will further support your wellness journey. If you have any questions about this medication, don’t hesitate to reach out to your healthcare professional for personalized advice.
Prescription Hydrochlorothiazide: An In-Depth Overview
Hydrochlorothiazide is commonly prescribed for managing hypertension and edema associated with various conditions, including heart failure and liver cirrhosis. This thiazide diuretic effectively lowers blood pressure by decreasing blood volume, which helps the heart work more efficiently. It’s available in tablet form and typically taken once daily, often in the morning to align with the body’s natural diuretic rhythm.
Dosage and Administration
The standard starting dose for adults is usually 12.5 mg to 25 mg, depending on the individual’s condition and response. It may be adjusted by healthcare providers based on blood pressure readings and potential side effects. Regular monitoring of blood pressure, electrolyte levels, and kidney function ensures optimal treatment and safety. Patients should follow the prescribed dosage without skipping or doubling doses to maintain stable blood pressure levels.
Side Effects and Precautions
Common side effects include dizziness, increased urination, and electrolyte imbalances, such as low potassium levels. Potentially serious effects, such as allergic reactions or severe skin rashes, require immediate medical attention. Inform healthcare providers about any pre-existing conditions, medications, or allergies before starting treatment. Staying hydrated and adhering to dietary recommendations can help mitigate some side effects, especially regarding electrolyte levels. Regular follow-ups are crucial to assess the ongoing effectiveness and safety of the treatment.
Clinical Indications and Dosage Guidelines for Hydrochlorothiazide
Hydrochlorothiazide primarily treats hypertension and edema. For hypertension, the standard starting dose is 12.5 mg once daily, which may be increased to 25 mg based on blood pressure response. In some cases, doses up to 50 mg may be used, especially for patients resistant to lower doses.
In managing edema associated with congestive heart failure or corticosteroid therapy, begin with a dose of 25 mg once daily. Adjust as necessary, with maximum dosages reaching 100 mg per day when required. It’s important to monitor renal function and electrolyte levels, particularly potassium and sodium, during treatment.
Doctors may recommend discontinuing use if blood pressure remains above target levels despite max dosing. Combine hydrochlorothiazide with other antihypertensive drugs for better control in patients with resistant hypertension. Regular follow-ups ensure optimal management of both blood pressure and any adverse effects.
Hydrochlorothiazide can be taken with or without food, offering flexibility for patient adherence. Encourage patients to maintain proper hydration and monitor their blood pressure at home for more effective management.
Potential Side Effects and Drug Interactions of Hydrochlorothiazide
Patients taking hydrochlorothiazide may experience a variety of side effects. Common ones include dry mouth, dizziness, and increased urination. Occasionally, more serious reactions such as electrolyte imbalances, severe allergic reactions, or kidney issues can occur. Monitor for symptoms like muscle cramps, confusion, or rapid heartbeat, as these may indicate significant imbalances in potassium or sodium levels.
Hydrochlorothiazide can interact with several medications, which may enhance its effects or increase the risk of side effects. Drugs such as lithium can lead to toxicity, while NSAIDs may reduce the effectiveness of hydrochlorothiazide by counteracting its diuretic action. Inform your healthcare provider about all medications, including over-the-counter options, to avoid potential interactions.
Some patients may experience interactions with other antihypertensive agents. Combining hydrochlorothiazide with ACE inhibitors or beta-blockers can enhance blood pressure control, but careful monitoring is required to prevent excessive blood pressure drops.
Regular blood tests are advisable to check electrolyte levels and kidney function to ensure safe and effective use of hydrochlorothiazide. If unusual side effects or symptoms arise, consult a healthcare professional promptly.