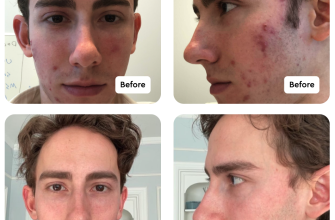
If you’re experiencing shedding while using Propecia and minoxidil, you’re not alone. Many users face this issue, which can be distressing. It’s crucial to remember that shedding may be part of your hair growth cycle. As old hair falls out, new hair can begin to grow in its place. This process, often referred to as “telogen effluvium,” typically occurs within the first few weeks or months of treatment.
Monitoring Your Progress is key. Tracking your hair’s condition helps you differentiate between normal shedding and potential concerns. Take photos periodically to capture changes and make it easier to discuss with a dermatologist if needed. Aim for patience during this phase; many users find that shedding reduces after the initial months, leading to thicker hair growth over time.
Consistency is essential. Apply minoxidil as directed, and take Propecia daily to achieve the best results. Skipping doses can hinder your progress, while sticking to your regimen can help stabilize your hair growth cycle. Keep an eye on any side effects and consult your healthcare provider if you notice anything unusual.
Stay informed about your treatment, and don’t hesitate to reach out to professionals for personalized advice. Understanding the shedding phase can help you feel more confident and optimistic about your hair restoration journey.
- Understanding Propecia and Minoxidil Shedding
- What Causes Shedding?
- What to Expect During Shedding
- What is Shedding in Hair Loss Treatments?
- Causes of Shedding
- What to Expect
- How Propecia Affects Hair Shedding
- Minoxidil Shedding: Causes and Duration
- Causes of Shedding
- Duration of Shedding
- Comparing Shedding Patterns: Propecia vs Minoxidil
- Shedding with Propecia
- Shedding with Minoxidil
- When to Expect Shedding After Starting Treatment
- Managing Shedding: Tips for Users
- Identifying Normal Shedding vs. Excessive Shedding
- Signs of Normal Shedding
- Signs of Excessive Shedding
- Long-Term Hair Growth: What to Expect After Shedding
- Consulting a Professional: When to Seek Help
- Signs You Should Consult a Professional
- What to Expect During a Consultation
Understanding Propecia and Minoxidil Shedding
Shedding is a common reaction when starting treatments like Propecia (finasteride) and Minoxidil for hair loss. It often surprises users, but this phase signals hair follicles transitioning into a new growth cycle.
What Causes Shedding?
As hair follicles respond to these medications, they may initially enter a telogen or resting phase, leading to increased hair fall. This is a temporary occurrence and should lessen within a few months as the body adjusts. Key points include:
- Propecia blocks DHT, which influences hair growth cycles.
- Minoxidil stimulates blood flow to hair follicles, prompting renewed activity.
- Both products can increase shedding as hair follicles reset.
What to Expect During Shedding
During shedding, you might notice more hair in your brush or shower. The amount of hair loss can vary, but it typically peaks around the 2-3 month mark after starting treatment. Consider these factors:
- Regular use of Propecia and Minoxidil is key to managing this phase.
- Patience is necessary; most individuals see improvement in 6-12 months.
- Consult your healthcare provider if shedding persists beyond 6 months.
Understanding the shedding phase can help manage expectations and encourage consistency in treatment, leading to better results over time.
What is Shedding in Hair Loss Treatments?
Shedding refers to the temporary increase in hair loss that some individuals experience after beginning hair loss treatments like Propecia or minoxidil. This phenomenon might seem alarming, but it often indicates that the scalp is undergoing a process of renewal. As weaker, thinner hairs fall out, the follicles prepare to promote healthier, stronger hair growth.
Causes of Shedding
The underlying reason for shedding is related to the hair growth cycle. Hair goes through three phases: anagen (growth), catagen (transitional), and telogen (resting). Starting treatment can shift hair from the resting phase to the shedding phase, leading to a noticeable loss for a short period. This shedding is usually a sign that hair follicles are responding to the treatment, and new hair will typically grow within a few months.
What to Expect
Individuals may experience shedding within the first few weeks or months of treatment. While this can be disheartening, it’s crucial to remain consistent with the treatment regimen. Shedding usually stabilizes within six months, and many report seeing significant improvement in hair density and thickness after one year of continued use. To enhance results, maintain a healthy lifestyle and consult with a healthcare provider about possible complementary treatments.
How Propecia Affects Hair Shedding
Propecia primarily reduces hair shedding by inhibiting the conversion of testosterone to dihydrotestosterone (DHT), which is a key factor in androgenetic alopecia. Users may experience an initial shedding phase known as “shedding”, where existing weak hairs fall out as newer, healthier hairs begin to grow. This is a normal part of the hair growth cycle and is often temporary.
Research shows that around 30-40% of users notice this transition at some point during the first few months of treatment. This shedding often occurs within the first three to six months, as the hair follicles undergo changes. These initial hairs are typically those that were already on their way out due to DHT’s effects.
The table below outlines the timeline and effects associated with Propecia treatment regarding hair shedding:
| Timeline | Effects |
|---|---|
| 0-3 Months | Initial shedding may occur; hair follicles start adjusting to DHT suppression. |
| 3-6 Months | Continued shedding possible; some users report noticeable hair regrowth. |
| 6-12 Months | Most users experience reduced shedding; hair density improves significantly. |
| 12+ Months | Hair stability; potential for continued improvement and less shedding observed. |
Staying consistent with the medication is key. If shedding persists beyond six months, consult a healthcare professional to assess the situation. They may recommend adjusting dosage or exploring additional treatments, such as minoxidil, which can complement Propecia’s effects.
Regular follow-ups with your healthcare provider ensure that hair health is monitored effectively, helping to navigate any unexpected reactions related to shedding during the Propecia treatment.
Minoxidil Shedding: Causes and Duration
Minoxidil shedding typically occurs as the scalp undergoes changes during the hair growth cycle. This process often begins within the first few weeks of using minoxidil. Shedding generally lasts from 2 to 8 weeks, but it can vary based on individual response and dosage.
Causes of Shedding
- Hair Growth Cycle: Minoxidil stimulates hair follicles, pushing existing hairs to enter the shedding phase, making way for new growth.
- Increased Blood Flow: Improved circulation enhances follicle activity, which can temporarily expel weak or dormant hairs.
- Product Response: Not everyone reacts the same way to minoxidil. Some users may experience more pronounced shedding as their hair adjusts to the treatment.
Duration of Shedding
- Initial Shedding: Most people notice shedding within the first couple of weeks, which is usually a sign that the treatment is working.
- Continuation: If shedding persists beyond 8 weeks, consider consulting a healthcare provider to ensure the use of minoxidil remains appropriate for your situation.
- Stabilization: After shedding, many users experience new hair growth typically within 3 to 6 months as the treatment takes effect.
Tracking your hair condition during treatment can provide insight into your progress. Remember to adhere to the recommended application and dosage for optimal results.
Comparing Shedding Patterns: Propecia vs Minoxidil
Propecia and minoxidil each produce unique shedding patterns that can impact users differently. Understanding these differences allows for better management of expectations during treatment.
Shedding with Propecia
Propecia primarily affects the hormone dihydrotestosterone (DHT), leading to hormonal changes that can cause initial shedding. This shedding often occurs within the first three months of usage as hair follicles transition to the anagen (growth) phase. Users should monitor this period closely, as it usually indicates that the treatment is working. After about six months, most users experience a decrease in shedding and improved hair density.
Shedding with Minoxidil
Minoxidil, on the other hand, may induce shedding sooner, typically within the first two weeks. This occurs as resting hair follicles push out existing hairs to allow for new growth. While this initial shedding can be alarming, it is a common response signaling that the treatment is activating the hair growth process. After approximately three to six months, users often see new hair growth and reduced shedding. Consistency in application is key for optimal results.
| Aspect | Propecia | Minoxidil |
|---|---|---|
| Onset of Shedding | 3 months | 2 weeks |
| Type of Shedding | Hormonal induced | Follicle activation |
| Duration of Shedding | Up to 6 months | 3 to 6 months |
| Expected Outcome | Improved hair density | New hair growth |
Both treatments involve a shedding phase, but the timeline and nature of this shedding differ. Users should stay informed and remain patient as their hair responds to these therapies.
When to Expect Shedding After Starting Treatment
Shedding typically occurs within 2 to 8 weeks after initiating treatment with Propecia or minoxidil. This initial phase may cause alarm, but it’s a common part of the hair growth cycle as weaker hair follicles make way for stronger, healthier ones.
As you progress, shedding should stabilize after around 12 weeks. Individual experiences will vary, so monitor your response and be patient during this adjustment phase. Remember, consistent use of the treatment is key to seeing improvement over the long term.
If shedding persists beyond 16 weeks or increases significantly, consult with a healthcare professional. They can assess your situation and recommend adjustments if necessary. Keeping track of your progress can help you to better understand your hair’s response to the treatment.
Managing Shedding: Tips for Users
Stay patient during the shedding phase. It’s a natural part of the hair growth cycle when using Propecia or minoxidil. Expect this period to last a few weeks to a couple of months as new hair pushes out older, weaker strands.
Maintain a consistent application routine. Use minoxidil exactly as directed, applying it to a dry scalp at least twice a day. This helps maximize absorption and minimizes the risk of excessive shedding.
Keep your scalp clean and healthy. Gently wash your hair and scalp to remove excess product buildup that may contribute to irritation or inflammation, which can exacerbate shedding.
Monitor your diet. Incorporate nutrient-rich foods that promote hair health. Omega-3 fatty acids, proteins, vitamins A, C, D, and E, along with minerals like zinc and iron, can support hair growth and reduce shedding.
Stay hydrated. Drinking enough water is vital for maintaining healthy hair and scalp, and it supports optimal blood circulation.
Reduce stress. Implement relaxation techniques such as meditation, yoga, or deep-breathing exercises. High stress can affect hair health, leading to increased shedding.
Consider hair-friendly products. Avoid harsh shampoos and conditioners that contain sulfates or alcohol. Opt for gentle, sulfate-free options that nourish rather than strip your hair of natural oils.
If shedding persists or worsens, consult a healthcare professional. They can evaluate your situation, adjust your treatment plan, or explore other underlying causes of hair loss.
Identifying Normal Shedding vs. Excessive Shedding
Monitor your hair shedding closely during the first few months of using Propecia and minoxidil. Normal shedding typically involves losing about 50 to 100 hairs daily. If you notice consistent shedding that exceeds this range, it may signal excessive shedding. Keep a journal to track the number of hairs lost daily and note any changes in product usage or lifestyle factors.
Signs of Normal Shedding
Normal shedding often follows a cyclical pattern. Increased loss may occur after starting treatment, commonly referred to as “shedding phase.” Hair regrowth usually appears within a few months. Check for signs of new growth, such as short, fine hairs in the shedding areas, which indicates that the treatment is working.
Signs of Excessive Shedding
Excessive shedding can manifest as thinning patches or bald spots rather than uniform hair loss. If you experience pain, itching, or inflammation alongside hair loss, consult a dermatologist. Additionally, pay attention to changes in the scalp condition or overall health, as these could be contributing factors. Address any underlying health conditions promptly, and discuss any concerns with your healthcare provider to adjust your treatment plan if necessary.
Long-Term Hair Growth: What to Expect After Shedding
Prepare for a significant transformation in your hair growth journey after experiencing shedding while using Propecia or minoxidil. The initial phase of shedding, often alarming, actually paves the way for stronger hair follicles to emerge.
Anticipate a gradual regrowth phase, typically beginning around three to six months post-shedding. During this time, new hair strands will appear, often finer at first but progressively thickening over the following months. Consistency in your application of minoxidil and adherence to your Propecia regimen are key factors in promoting optimal growth.
Monitor your hair density closely. Visible results usually start to surface between six to twelve months, with continued improvement often extending to eighteen months or longer. Patience is essential; hair growth varies widely among individuals based on genetics and lifestyle.
Incorporate a balanced diet rich in vitamins and minerals to support the hair growth process. Consider supplements like biotin or zinc, as these can enhance follicle health. Additionally, maintaining a stress-free environment and getting adequate sleep will positively influence your results.
Regularly check in with a healthcare professional to assess your progress. They can provide personalized advice and make adjustments to your treatment plan if necessary. Remember, while shedding can be unsettling, it’s often a positive precursor to healthier hair.
Consulting a Professional: When to Seek Help
If you experience significant shedding while using Propecia or Minoxidil, consulting a healthcare professional is advisable. Recognizing the signs that indicate a need for expert advice can save time and alleviate concerns.
Signs You Should Consult a Professional
- Persistent Shedding: If hair loss continues beyond the initial few weeks of treatment.
- Scalp Irritation: Noticeable redness, itching, or discomfort in the treated areas.
- Lack of Progress: Failure to see any improvement in hair growth after several months of consistent use.
- Abnormal Symptoms: Any unexpected side effects such as dizziness, chest pain, or changes in libido.
What to Expect During a Consultation
During your appointment, be prepared to discuss your medical history and hair loss concerns. The specialist may conduct a physical examination of your scalp and perform tests to determine the cause of your shedding.
- Personalized Evaluation: A tailored assessment of your specific situation will guide treatment recommendations.
- Alternative Solutions: Exploring other medications or therapies if the current treatment is ineffective.
- Regular Monitoring: Setting up follow-up appointments to track your progress and make necessary adjustments.
Proactive communication with a healthcare provider can lead to more effective management of hair loss and ensure a better outcome.