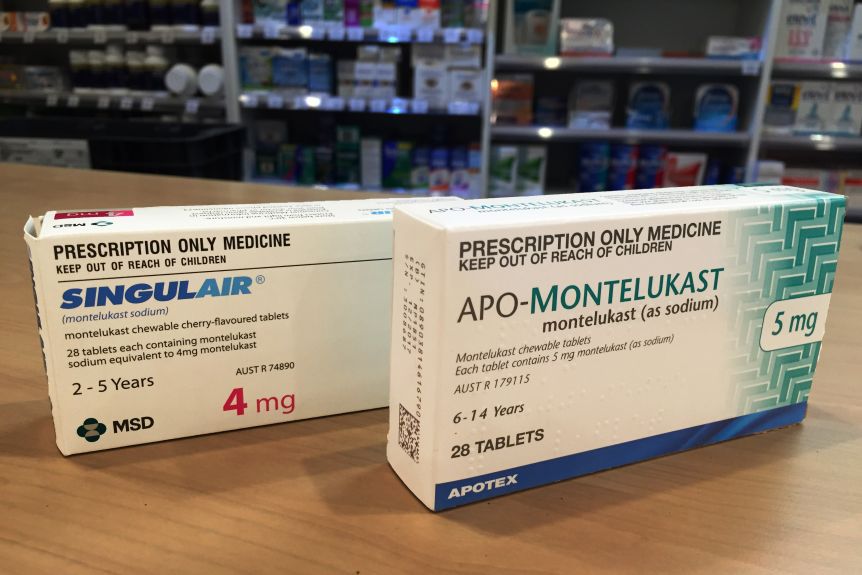
Choosing Singulair requires a prescription from your healthcare provider. This medication plays a significant role in managing asthma and allergic rhinitis symptoms, making it a go-to option for many patients seeking relief.
Understanding the necessity for a prescription emphasizes the need for professional guidance. Your doctor will assess your specific health needs, reviewing any pre-existing conditions and potential interactions with other medications. This careful evaluation helps tailor the treatment to achieve optimal results.
When discussing Singulair, dosages may vary based on individual circumstances. Always follow your doctor’s instructions regarding when and how to take it. Regular follow-ups can ensure that the treatment continues to meet your needs effectively, adjusting as necessary based on your response.
Engaging with your healthcare provider keeps you informed about possible side effects and what to watch for during treatment. Having open conversations can lead to better outcomes and a clearer understanding of how Singulair fits into your overall health plan.
- Singulair by Prescription Only
- Understanding Singulair and Its Uses
- Why Singulair Requires a Prescription
- Medical Supervision
- Dosage and Administration
- Potential Side Effects of Singulair
- Who Should Consider Taking Singulair?
- Asthma Management
- Allergies and Seasonal Issues
- How to Obtain a Prescription for Singulair
- Discussing Treatment Options
- Receiving the Prescription
- Alternatives to Singulair for Allergy and Asthma Management
Singulair by Prescription Only
Singulair, an oral medication commonly used to manage asthma and seasonal allergies, is available by prescription only. This restriction ensures proper evaluation and monitoring by a healthcare professional. Consulting with your doctor is the first step to determine if Singulair is appropriate for your condition.
During your consultation, your doctor will review your medical history, existing medications, and overall health status. This assessment helps to identify potential interactions and contraindications. If deemed suitable, your doctor will provide a prescription tailored to your needs.
Adhering to the prescribed dosage is crucial. Singulair typically comes in chewable tablets or granules, making it easier for different age groups to take. Ensure you follow the instructions for administration, especially when it involves children or individuals with difficulty swallowing pills.
Regular follow-ups are necessary to monitor your response to the medication. Your doctor may adjust the dosage or switch to an alternative if needed. Report any side effects or concerns during your treatment to facilitate timely adjustments.
Access to Singulair solely through a prescription emphasizes responsible use. This approach fosters a thorough understanding of the medication’s benefits and risks, supporting individuals in managing their health effectively.
Understanding Singulair and Its Uses
Singulair plays a key role in managing asthma and allergic rhinitis by blocking leukotrienes, which are chemicals in the immune system that contribute to inflammation and mucus production. Patients often find relief from symptoms such as wheezing, shortness of breath, and nasal congestion when using this medication.
This prescription-only drug is typically indicated for individuals aged 12 months and older. It is available in various formulations, including chewable tablets for children and film-coated tablets for adults, which allows for flexibility depending on patient needs.
Patients tend to take Singulair once daily, generally in the evening, which aligns with the body’s natural rhythms of asthma symptoms. Consistency is crucial; regular use ensures optimal control over symptoms and may improve quality of life.
While many individuals experience positive outcomes, some may encounter side effects such as headache, abdominal pain, or fatigue. It’s essential to discuss with a healthcare provider if any side effects become bothersome or persistent.
Monitoring for mood changes is also necessary, as there have been reports of behavioral changes associated with Singulair. Always consult a healthcare professional if you or your child experience mood swings or unusual behavior.
For maximum benefit, Singulair must be part of a broader asthma management plan that includes avoiding triggers and adhering to prescribed inhalers or other medications. Regular check-ins with a healthcare provider can help tailor the treatment approach to achieve the best results.
In summary, Singulair serves as a valuable tool for controlling asthma and allergies. Engaging with a healthcare provider helps ensure its appropriate use and enhances overall treatment effectiveness.
Why Singulair Requires a Prescription
Singulair, or montelukast, is prescribed primarily for its targeted action in managing asthma symptoms and allergic rhinitis. The need for a prescription stems from several important factors.
Medical Supervision
Using Singulair necessitates medical oversight to ensure safety and efficacy. Healthcare professionals evaluate patient history, potential drug interactions, and any pre-existing conditions before prescribing. This step is crucial to minimize the risk of side effects and optimize treatment outcomes.
Dosage and Administration
- Singulair comes in various forms, including chewable tablets and granules. The correct formulation depends on the patient’s age and specific health needs.
- Precise dosing is vital. A physician prescribes the appropriate dose based on individual factors, which helps maintain therapeutic effectiveness while reducing the chance of adverse reactions.
Singulair also has potential side effects, necessitating communication between the patient and healthcare provider. Regular follow-ups allow for dosage adjustments and monitoring of any emerging symptoms. For these reasons, using Singulair without a prescription is not advisable. Seek guidance from a healthcare professional for safe and effective management of your condition.
Potential Side Effects of Singulair
Patients taking Singulair may experience various side effects. Common ones include headaches, which can occur in about 15% of users. Drowsiness and fatigue are also reported, potentially affecting daily activities. Some individuals notice digestive issues, such as nausea or diarrhea, with gastrointestinal symptoms varying in intensity.
Psychological effects have gained attention. Users may report feelings of anxiety, depression, or changes in mood. While these occurrences are rare, it’s important to monitor mental health closely during treatment. Keep an open line of communication with healthcare providers regarding any emotional changes.
More serious side effects can include allergic reactions, characterized by hives, swelling, or difficulty breathing. If any of these symptoms develop, seek medical help immediately. Rare cases of liver function changes have also been documented, so regular check-ups may be recommended.
Patients should consider factors such as pre-existing conditions and ongoing medications that might interact with Singulair. Discuss individual risks with a healthcare provider to manage potential side effects effectively. Close monitoring and timely reporting of any unexpected symptoms can enhance safety during treatment.
Who Should Consider Taking Singulair?
Singulair is primarily recommended for individuals experiencing asthma or allergic rhinitis. Consult your healthcare provider if you fit into one of these categories:
Asthma Management
- People with persistent asthma symptoms that interfere with daily activities.
- Individuals needing an additional medication to control asthma alongside other treatments.
- Children aged 12 months and older who suffer from asthma may also benefit.
Allergies and Seasonal Issues
- Those dealing with seasonal allergies who seek relief from symptoms like sneezing or nasal congestion.
- Individuals with year-round allergic rhinitis looking for consistent management of their symptoms.
Consider discussing with your doctor if you have any of the following conditions: liver problems, a history of mental health issues, or if you are pregnant or breastfeeding. Your healthcare provider will assess whether Singulair fits your specific health needs and treatment goals.
How to Obtain a Prescription for Singulair
Schedule an appointment with your healthcare provider to discuss your symptoms related to allergies or asthma. Describe your medical history and explain how these conditions affect your daily life. Be honest about any previous treatments you have tried and their outcomes, as this information helps your provider make an informed decision.
Discussing Treatment Options
Your provider will assess whether Singulair is suitable for you based on your specific needs. Ask questions about the medication, its side effects, and how it works. Make sure to mention any other medications you are currently taking to avoid potential interactions.
Receiving the Prescription
If Singulair is recommended, your provider will write you a prescription. You can then take this prescription to your local pharmacy. Some providers may also send prescriptions electronically. If you have questions about dosage or how to take the medication, don’t hesitate to ask your pharmacist for clarification.
Once you start taking Singulair, monitor your symptoms and report any unusual side effects to your provider. Regular follow-up appointments may be necessary to adjust your treatment plan as needed.
Alternatives to Singulair for Allergy and Asthma Management
Consider using inhaled corticosteroids such as fluticasone or budesonide. They reduce inflammation in the airways, providing long-term control of asthma symptoms. Regular use can significantly improve lung function.
Leukotriene receptor antagonists like zafirlukast offer a similar mechanism to Singulair but come with different profiles. They can help alleviate allergy and asthma symptoms without some of the side effects associated with other medications.
Short-acting beta-agonists (SABAs) such as albuterol serve as quick relief during asthma attacks. They work rapidly to dilate airways, making them a staple for individuals with intermittent symptoms.
Antihistamines like cetirizine and loratadine are beneficial for managing allergy symptoms. They alleviate nasal congestion and itching, making them ideal during allergy season.
Combination inhalers that include both corticosteroids and long-acting beta-agonists (LABAs) like salmeterol offer comprehensive management for asthma. These medications address both inflammation and bronchoconstriction, providing better control.
| Medication Type | Examples | Use |
|---|---|---|
| Inhaled Corticosteroids | Fluticasone, Budesonide | Long-term inflammation control |
| Leukotriene Receptor Antagonists | Zafirlukast | Allergy and asthma symptom relief |
| Short-acting Beta-agonists | Albuterol | Quick relief during attacks |
| Antihistamines | Cetirizine, Loratadine | Allergy symptom management |
| Combination Inhalers | Salmeterol with Fluticasone | Comprehensive asthma control |
Always consult a healthcare provider to tailor the management plan to individual needs. Each option has distinct benefits and risks, ensuring that users receive the most suitable treatment for their condition.