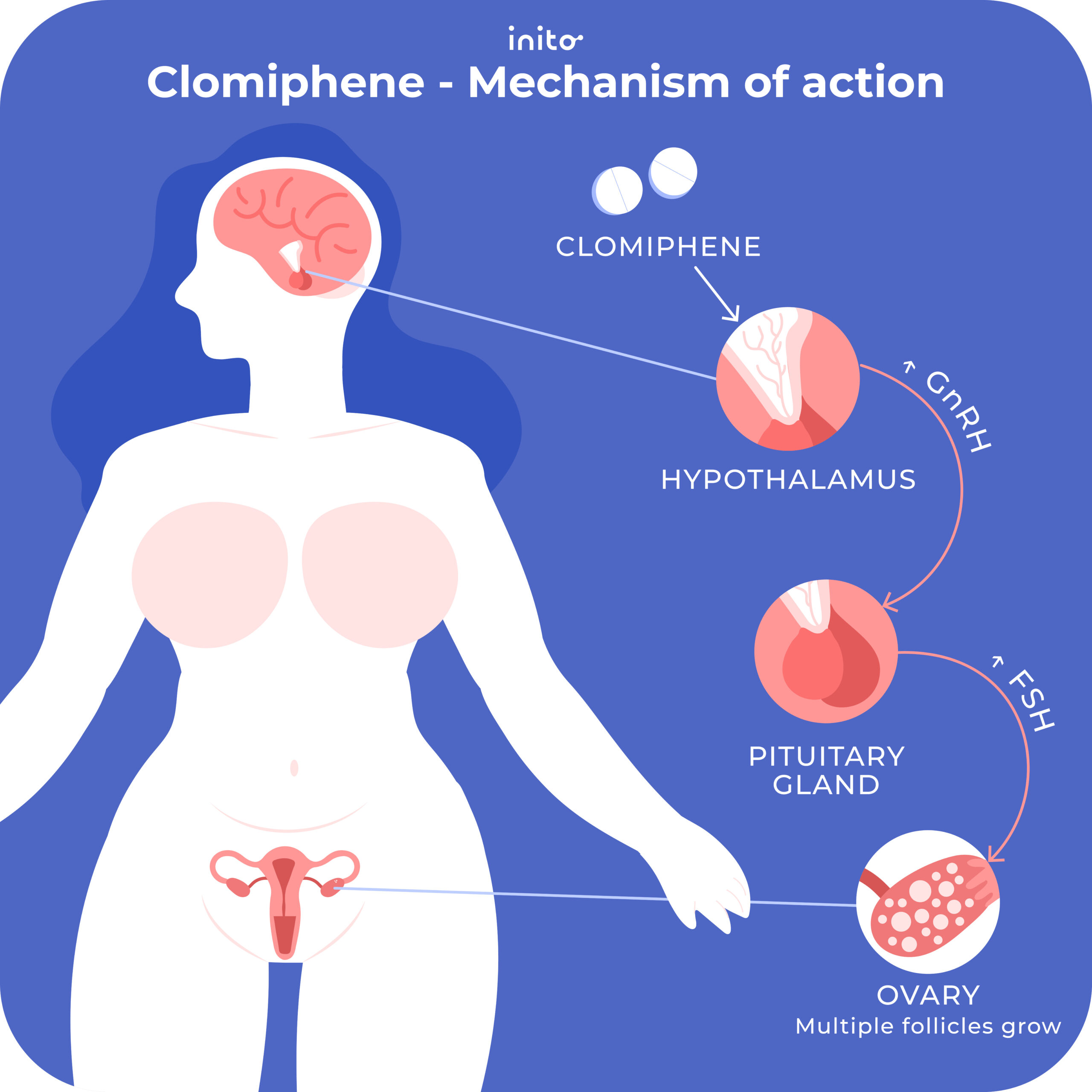
For those dealing with slow-growing follicles during fertility treatments, Clomid often emerges as a crucial option. Clomid (clomiphene citrate) acts by stimulating the release of hormones necessary for ovulation, making it essential for enhancing follicle development. Tracking follicle growth can help determine the right timing for insemination or IVF procedures.
Monitoring follicle size is vital. A typical follicular size for ovulation is around 18-24 mm. Slow-growing follicles may not reach this size despite Clomid treatment. In such cases, additional monitoring can provide insight into hormonal levels, including estradiol, that could influence the growth rate. Adjustments to the Clomid dosage or a break before the next cycle can help manage persistent slow growth.
Consider lifestyle factors that may impact follicle development. Adequate nutrition, stress management, and regular exercise can contribute positively to ovarian function. Furthermore, collaborating closely with a healthcare provider ensures personalized guidance throughout the treatment process. Each person’s response to Clomid varies, and understanding individual patterns can lead to better outcomes.
- Understanding Slow Growing Follicles and Clomid Treatment
- How Clomid Works
- Monitoring Follicle Development
- What are Slow Growing Follicles?
- How Clomid Affects Follicle Development
- Identifying Slow Growing Follicles During Treatment
- Strategies to Enhance Follicle Growth with Clomid
- Monitor Hormonal Levels
- Consider Timing and Dosage
- When to Consult a Specialist About Slow Growing Follicles
Understanding Slow Growing Follicles and Clomid Treatment
Slow growing follicles can hinder the process of ovulation, making it challenging for individuals trying to conceive. Clomid, or clomiphene citrate, is often prescribed to stimulate follicular development and increase the chances of ovulation.
How Clomid Works
Clomid acts as a selective estrogen receptor modulator. It binds to estrogen receptors in the hypothalamus, tricking the body into thinking estrogen levels are low. This action prompts the release of hormones that stimulate follicle growth.
- Typically prescribed for a 5-day course, starting on day 3, 4, or 5 of the menstrual cycle.
- Common dosages range from 50 mg to 150 mg per day, adjusted based on individual response.
Monitoring Follicle Development
Regular monitoring during Clomid treatment is vital for assessing the response. Ultrasounds can measure follicular growth, determining when ovulation is likely to occur.
- Follicles should ideally grow at a rate of 1-2 mm per day.
- An optimal size for triggering ovulation is typically around 18-24 mm.
Slow growing follicles may require adjustments in dosage or additional treatments. Working closely with a healthcare provider is essential for personalized care.
Consider lifestyle factors that may impact follicle development, such as nutrition, stress management, and maintaining a healthy weight. A holistic approach supports Clomid’s effectiveness.
What are Slow Growing Follicles?
Slow growing follicles refer to ovarian follicles that develop at a slower rate than the average during the menstrual cycle. These follicles may not reach optimal size or maturity for ovulation, which can affect fertility. Typically, follicle growth is monitored via ultrasound, where specialists track the size and number of follicles.
Follicles usually grow at a pace of about 1-3 mm per day. However, slow growing follicles can progress at a rate of less than 1 mm daily. This slower development often indicates underlying hormonal imbalances or issues with ovarian response. Identifying and monitoring these follicles becomes important during fertility treatments, such as those involving Clomid, which aims to stimulate healthy growth.
Women experiencing irregular menstrual cycles or hormonal fluctuations may be more prone to slow growing follicles. Anovulation, a condition where no eggs are released, can also stem from or contribute to this issue. Evaluating overall reproductive health, including hormone levels and follicle sizes, is crucial for effective planning of fertility interventions.
To enhance the chances of developing healthy follicles, incorporating lifestyle changes can make a substantial difference. Maintaining a balanced diet rich in vitamins and minerals, managing stress through relaxation techniques, and ensuring regular physical activity all contribute positively to reproductive health. Additionally, consulting with healthcare professionals about medications and treatment options tailored to individual needs is a wise step forward.
How Clomid Affects Follicle Development
Clomid stimulates follicle development by blocking estrogen receptors in the hypothalamus, leading to increased secretion of gonadotropins. This boost in follicle-stimulating hormone (FSH) encourages the growth of ovarian follicles. As a result, larger and more mature follicles often form, which can enhance the chances of ovulation.
While many experience positive outcomes, some may see slow-growing follicles as a response to Clomid. This scenario can occur if the dosage is too low, resulting in insufficient stimulation. Adjusting the dosage can promote optimal follicular response, ensuring that the follicles grow appropriately.
Monitoring through ultrasound during a Clomid cycle provides essential feedback on follicle size and number. Regular evaluations can guide adjustments to dosage, helping to achieve a balanced approach to treatment. A healthcare provider’s oversight is critical in determining the right protocol for individual needs.
Utilizing Clomid also impacts the hormonal balance, potentially leading to variations in cycle regularity. While many achieve ovulation, some may still encounter anovulation or delayed ovulation. Tracking ovulatory signs, such as basal body temperature and cervical mucus changes, can provide insights into your cycle’s progression and follicle readiness.
Patient education plays a key role in understanding how Clomid influences follicle development. Discussing expectations and any concerns with a healthcare professional can lead to a more tailored approach, enhancing the overall experience of treatment. By actively participating in the process, individuals can better navigate the complexities of their fertility journey.
Identifying Slow Growing Follicles During Treatment
Monitor follicular growth closely with regular transvaginal ultrasounds. Aim for assessments every two to three days during the follicular phase. Pay attention to the size of follicles; those growing slowly may not reach the optimal size for ovulation. Typically, follicles should grow about 1-2 mm per day.
Evaluate hormone levels to identify potential issues. Measure estradiol levels alongside ultrasound findings. Low estradiol in the presence of slow-growing follicles can indicate suboptimal ovarian response. Adjust treatment protocols based on these results to enhance follicular development.
Consider the quality of the medication. Clomid can impact different individuals differently, so discussing dosage with your healthcare provider is key. If slow-growing follicles persist, explore alternatives or add medications like gonadotropins to stimulate growth.
Keep an eye on overall health. Factors such as stress, weight, and lifestyle choices influence follicle development. Ensure a balanced diet, regular exercise, and proper hydration to support ovarian function.
Communication with your healthcare team fosters a better understanding of your specific situation. Share observations or concerns regarding follicular growth. This partnership allows for tailored adjustments to maximize your treatment’s success.
Strategies to Enhance Follicle Growth with Clomid
Maintain a healthy lifestyle to optimize the effectiveness of Clomid. Focus on balanced nutrition, regular exercise, and adequate hydration. A well-rounded diet rich in antioxidants, healthy fats, and protein supports overall reproductive health and may improve follicle response.
Monitor Hormonal Levels
Regularly assess hormonal levels through blood tests. Monitoring estrogen, progesterone, and follicle-stimulating hormone (FSH) can provide insights into your response to Clomid. Adjustments to dosage or timing can be made based on these results.
Consider Timing and Dosage
Timing Clomid administration carefully can influence follicle growth. Typically, Clomid is taken for five days, starting on the second, third, or fourth day of the menstrual cycle. Consult a healthcare provider to determine the most effective dosage based on individual responses.
| Day of Cycle | Clomid Dosage (mg) | Monitoring |
|---|---|---|
| 3 | 50 | Follow-up ultrasound |
| 5 | 100 | Blood tests |
| 7 | 150 | HCG trigger shot |
Incorporate stress management techniques like yoga or meditation. Reducing stress can positively influence hormone levels and enhance follicle development. Engage in activities that bring relaxation and joy, facilitating a more favorable environment for successful ovulation.
When to Consult a Specialist About Slow Growing Follicles
If you notice that your follicles are growing slowly, it’s important to seek help from a specialist. Signs such as irregular menstrual cycles, inconsistent ovulation, or difficulty conceiving signal the need for an evaluation. A healthcare provider can conduct ultrasounds and hormone tests to assess follicular development.
If you have been on Clomid for several cycles without success, consulting a reproductive endocrinologist is advisable. They can determine whether there are underlying issues affecting your response to the medication. Additionally, if you experience significant discomfort or side effects from Clomid, report these symptoms immediately for a proper assessment.
Should you have conditions like polycystic ovary syndrome (PCOS) or a history of hormonal imbalances, proactive medical guidance becomes important. Specialists can offer tailored strategies to enhance follicle growth and improve overall fertility outcomes.
Consider scheduling an appointment if you have concerns about your ovarian reserve or if your age impacts your fertility journey. Regular monitoring can provide valuable insights into your reproductive health and help create a feasible plan moving forward.
Open communication with your healthcare provider enables you to make informed decisions about your fertility treatment. Don’t hesitate to voice your concerns; timely consultations can be a key step toward achieving your goals. Remember, monitoring and professional advice can make a significant difference in your fertility experience.